VNC (Virtual Network Computing) is a system for remote access to a computer's desktop. VNC allows you to send keyboard keystrokes and mouse movements from one computer to another, and to relay screen content over a computer network.
VMmanager uses VNC to remotely manage virtual machines (VMs).
VNC does not support clipboard transfer.
Connecting to a VM via VNC
You can connect to a VM:
- through the platform interface;
- using a third-party VNC client. For example, RealVNC Viewer or TightVNC.
Connecting from the VMmanager interface
- Enter Virtual machines → select the VM →
 menu → VNC. The VM desktop opens in a new browser tab.
menu → VNC. The VM desktop opens in a new browser tab. - Enter the login and password to connect to the VM. If you do not know the login or password, request this information from your service provider.
Connecting with a VNC client
Connection example for RealVNC Viewer:
- Download and install the version of RealVNC Viewer for your operating system.
- Start RealVNC Viewer and create a connection to the VM:
- Enter File → New connection.
-
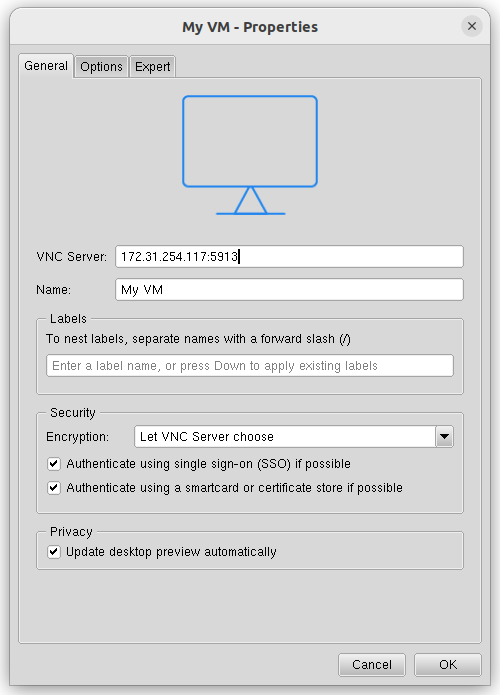
In the VNC Server field, enter the IP address and port of the VNC server, separated by a colon.
Connection settings are defined by the platform administrator. To create a connection, ask your service provider for the VNC server details: address, connection port, and password. - In the Name field, enter an arbitrary name for the connection.
-
Press OK.
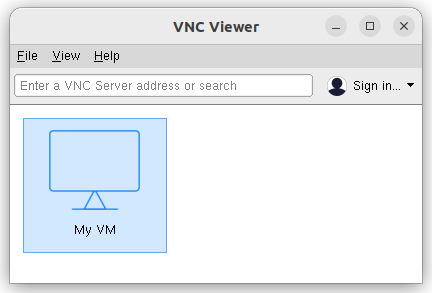
- To connect to a VM, double-click the connection icon.
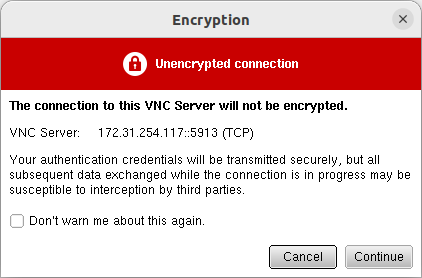
- If RealVNC Viewer displays a warning about an unsecured connection, press Continue.
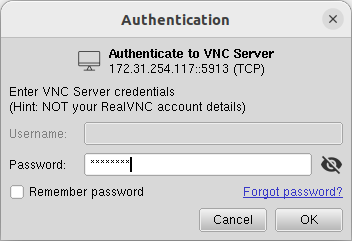
- In the Password field, enter the password for the VNC server and press OK.
- Enter the login and password to connect to the VM. If you do not know the login or password, request this information from your service provider — a company that provides you the virtual server service.
 En
En
 Es
Es