IPmanager is a control panel for IP address management. In order to work with IPs, you need to add them to IPmanager. For this, go to Dashboard → Networks.
Create a network
Click on Add to create a new network.
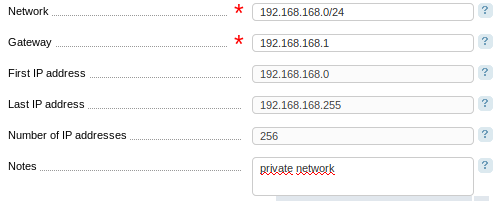
Specify:
- Network — IPv4 or IPv6 network in the format <subnet address>/<mask>. The system will automatically calculate First IP address, Last IP address, and the Number of IP addresses;
- Gateway — the gateway address which must belong to the network you are adding;
- Notes — any additional information can be added here and will be represented in the column Notes.
Add the string "Option DisableGatewayChecking" to the IPmanager configuration file (/usr/local/mgr5/etc/ipmgr.conf per default) to disable checking whether the gateway belongs to the network being added.
Create reverse domain zones
When you add a new network, IPmanager will automatically add reverse domain zones. Read more in Reverse domain names. The system will use the parameters specified in Settings → DNS server. Read more in DNS server settings.
The mask prefix will always be a maximum number but lower or equal to the mask prefix of the IP network.
IPv4
IPmanager can work with prefixes /8, /16, /24 for IPv4 networks. When you create a network with /23, two reverse domain zones will be created with /24. Accordingly, when you create a network with /14, four domain zones with /16 will be created. When you create a network with the mask lower than /24, the system will create either a network with /24 or classless reverse domain zone with the mask prefix equal to the prefix of the network you create.
IPv6
IPmanager can work with prefixes /12, /16, /20, /24, /28, /32, /48, /64 for IPv6 networks. When you create a network with /47, two reverse domain zones will be created with /48. Accordingly, when you create a network with /49, 32768 domain zones with /64 will be created. When you create a network with the mask lower than /64, the system will create either a network with /64 or classless reverse domain zone with the mask prefix equal to the prefix of the network you create.
Manage networks
Click on IPs to view the list of all network IPs.
Add a new address
This list contains IP addresses that have a status in IPmanager. In order to add an address that is already used, you need to initialize it. For this, click on Add.
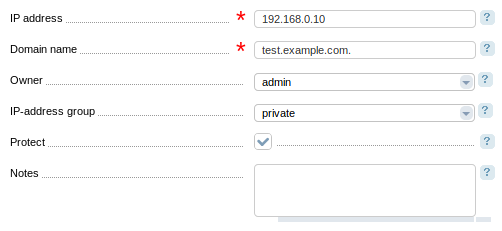
Specify:
- IP address;
- Domain name — a name that corresponds to the IP address;
- Owner — a user that the IP address belongs to.
- IP-address group — a group that the IP address belongs to. This field is only available when you select a user in the Owner field;
- Protect — this option gives the status "Protected (very important)" to the IP address. The address with such a status cannot be deleted or given for another usage;
- Notes — any additional information that will be represented in the list of network addresses in the column Notes.
IP address statuses
IPmanager can give the following statuses to its IPs:
- Free — the address is available and has passed through the check. Read more in Check IP addresses;
- Reserved — the address is being used;
- Service — the address is reserved for special usage. Service IPs cannot be used for provisioning. This status is given to a network address (the first address in the network), a gateway address specified when you add a new network, a broadband address (the last address in the network), and addresses on network borders with the mask prefix /24 for IPv4 addresses. The addresses on borders are being reserved because some operating systems might have problems when working with them.
E.g. when you add the network 192.168.0.0/23, the following addresses will be reserved:- 192.168.0.0 — network address;
- gateway address;
- 192.168.0.255 — broadband address for the subnet 192.168.0.0/24;
- 192.168.1.0 — network address for the subnet 192.168.1.0/24;
- 192.168.1.255 — broadband address.
- Being checked — the address is unassigned but has not passed through the check yet. Read more in Check IP addresses;
- Blocked by DNSBL — the address has not passed through the check of presence in DNSBL blacklists. Read more in the articles Check IP addresses, DNSBL blacklists;
- Used in network — the address has not passed the check for physical availability in the network;
- Protected (very important) — the address cannot be deleted or given for another usage.
Click on Unassign to make the IP address "Free".
 En
En
 Es
Es