With VMmanager, you can provide users with a SaaS service – deploying virtual machines with preinstalled software. Ilya Kalinichenko, VMmanager DevOps, tells how to arrange automatic CI/CD provisioning using the platform.
VMmanager supports shell scripts. You can set variables for them. When creating a virtual machine, VMmanager will automatically request variable values from users or generate them automatically.
Let us configure the service to automatically provide virtual machines with a ready development environment. To do this, we will create a script that will install Gitlab and Mattermost. Gitlab has everything developers need to work together:
- Git repository;
- a convenient portal with different permission levels;
- a built-in system for integration and deployment automation.
Mattermost — is a free equivalent of Slack. Developers love to discuss products, plan, design, and just talk, and Mattermost is great for that.
Preparing a script to install Gitlab and Mattermost
# Install the SSH server
yum install -y curl policycoreutils openssh-server openssh-clients
systemctl enable sshd
systemctl start sshd
# Open ports 22, 80 and 443 in the firewall
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ssh
systemctl reload firewalld
# Install Postfix
yum install postfix -y
systemctl enable postfix
systemctl start postfix
# Install the Gitlab repository
curl -sS https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | bash
if [ -z "($GITLAB_URL)" ] || [ "($GITLAB_URL)" = "()" ]; then
GITLAB_URL=gitlab.example.com
else
GITLAB_URL="($GITLAB_URL)"
fi
if [ -z "($MM_URL)" ] || [ "($MM_URL)" = "()" ]; then
MM_URL=mattermost.example.com
else
MM_URL="($MM_URL)"
fi
# Install Gitlab
EXTERNAL_URL="$GITLAB_URL" yum install -y gitlab-ce
# Enable Mattermost and configure it
sed -i "/mattermost_external_url/cmattermost_external_url 'http://$MM_URL'" /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
sed -i "/mattermost\['enable'\]/cmattermost['enable'] = true" /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
sed -i "/mattermost_nginx\['enable'\]/cmattermost_nginx['enable'] = true" /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
sed -i "/letsencrypt\['enable'\]/cletsencrypt['enable'] = false" /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
sed -i "/package\['modify_kernel_parameters'\]/cpackage['modify_kernel_parameters'] = false" /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
# Launch reconfiguration so that Gitlab creates all necessary files and settings
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Configuring the settings in VMmanager
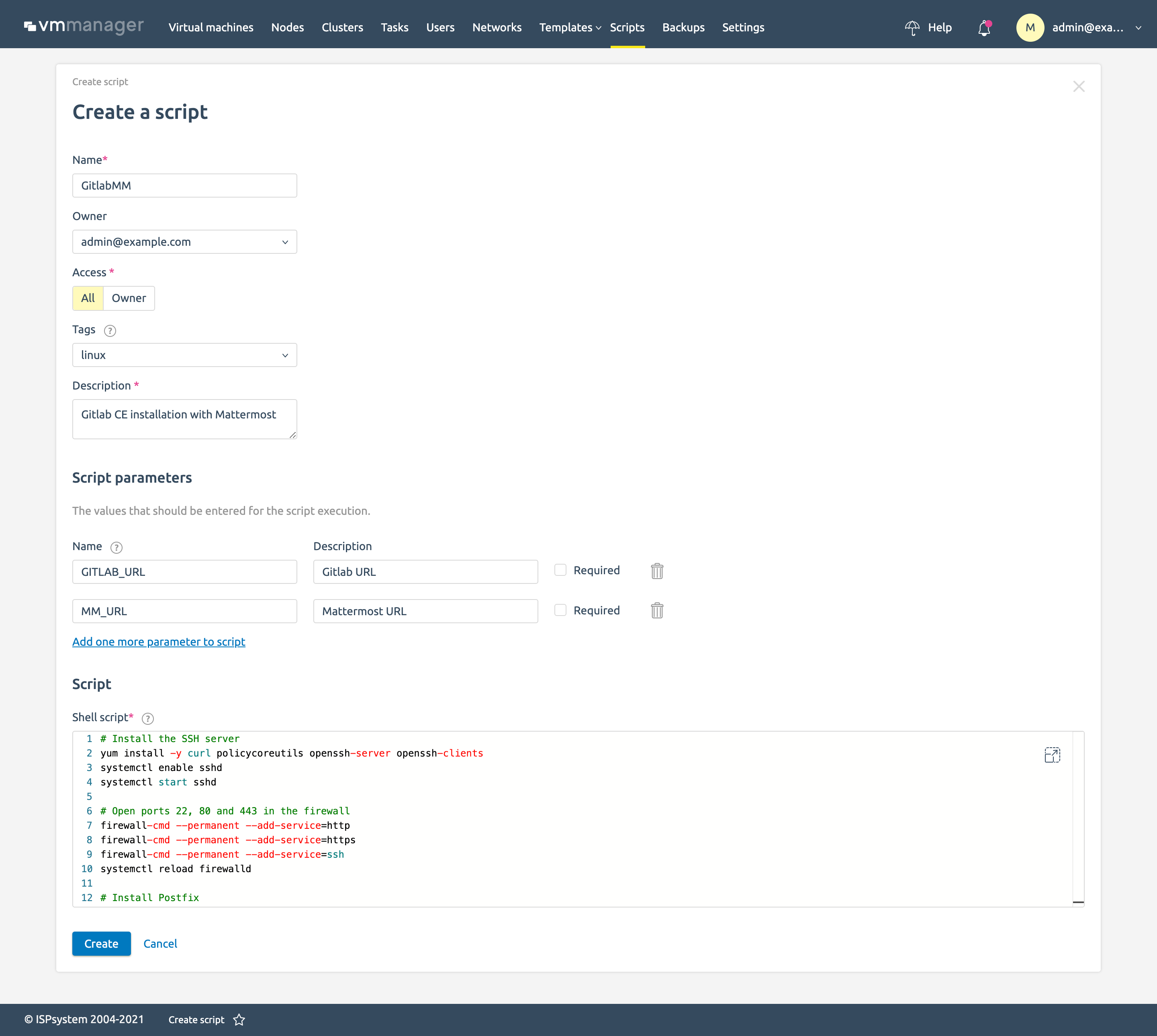
In the platform, open the script list and create a new script:
- Name — name of the script which the clients will see.
- Owner — VMmanager user who will be updating the script as required.
- Access — to all or the Owner only. Here you can temporarily disable client access to the script to debug something.
- Tags are used to designate the OS for which the script will be available. We will enable it here for CentOS 7 and CentOS 8.
- A Brief description that the client will see in the list of scripts..
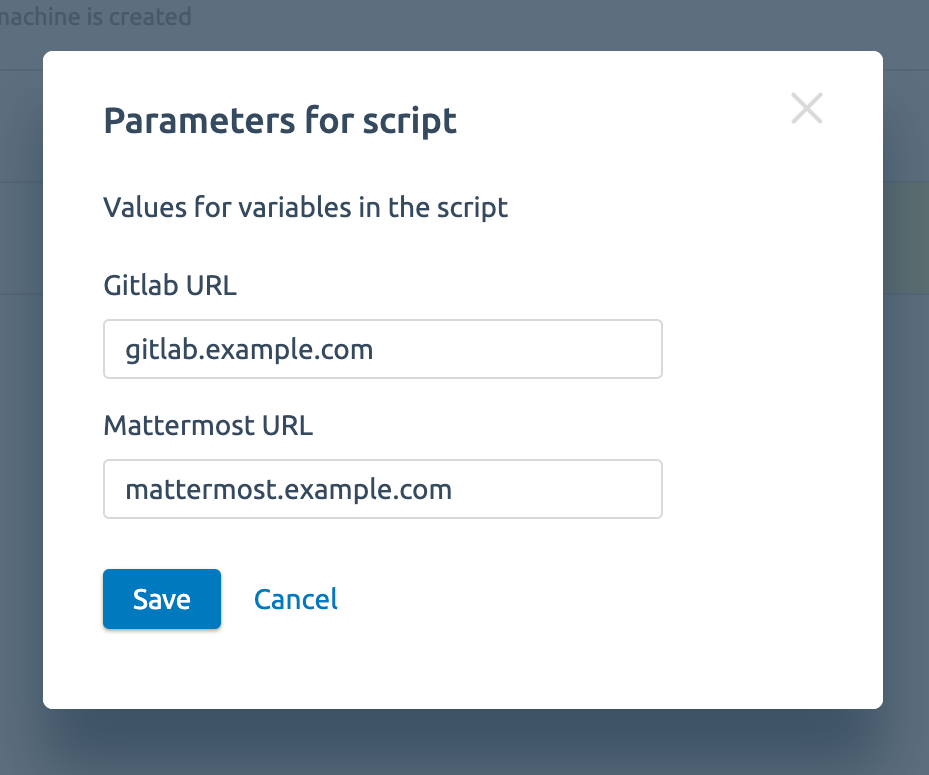
- The Script parameters are variables. VMmanager will request them from users when launching the script. We have two such variables:
GITLAB_URL — here you will need to specify the domain on which Gitlab will run.
MM_URL — here you will need to specify the domain on which Mattermost will run.
When the end user orders a service, VMmanager will request this data from him. - Script — here the script itself will be written. An example I tested on CentOS 8.
Let us check if the script works
Run the script on a freshly installed VM. Note that GItlab is a large application that needs at least 4 cores and 4GB RAM.
System requirements for Gitlab
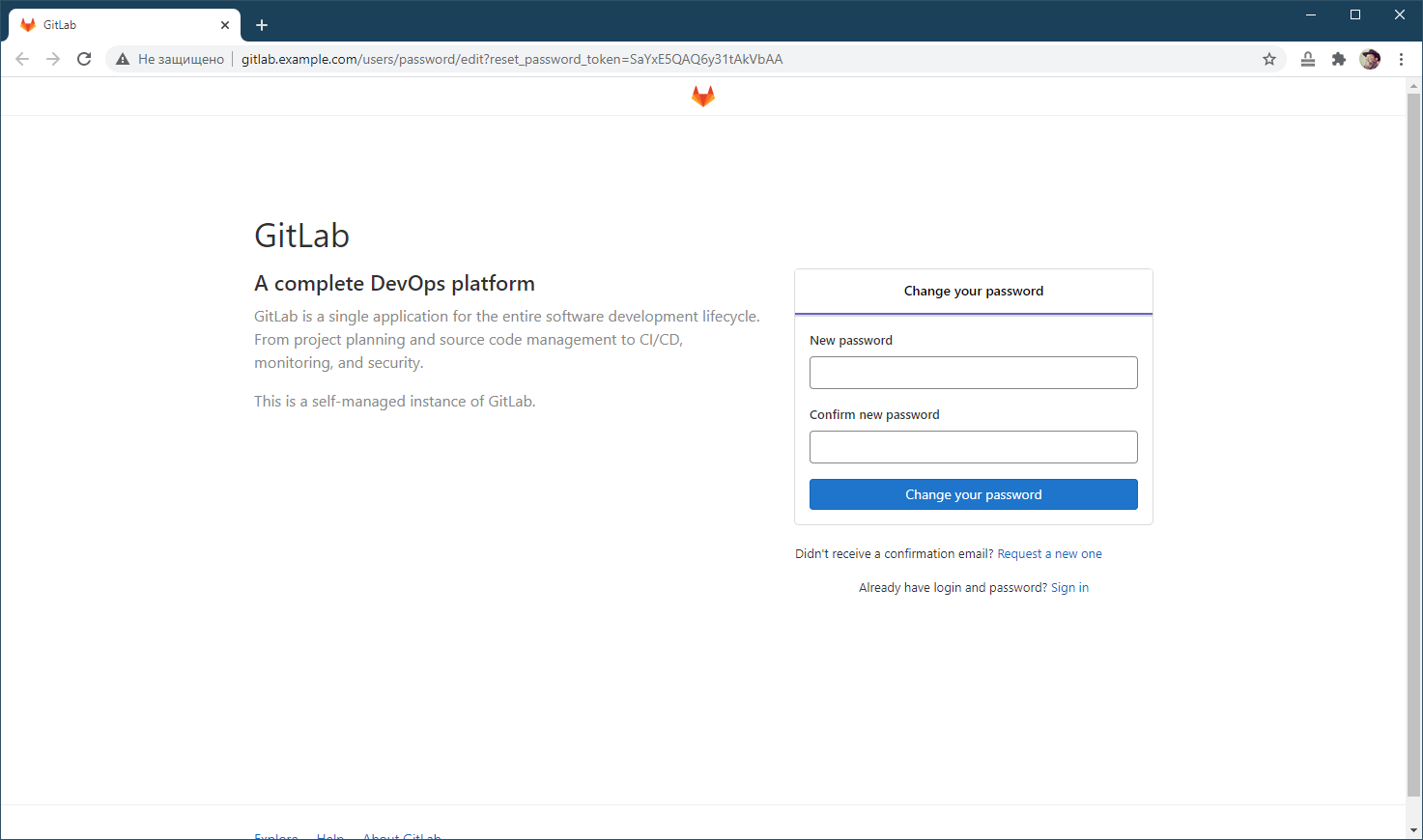
After the script is completed, go to http://gitlab.example.com or http://mattermost.example.com in your web browser for further configuration.
Scripts in VMmanager. Documentation
Try VMmanager for automatic sale of SaaS and VPS hosting
VMmanager is a platform for virtualization and automatic provisioning of virtual machines.