QEMU Guest Agent is a daemon program that is installed on a VM. QEMU Guest Agent provides execution of commands on VMs and information exchange between VMs and the cluster node.
VMmanager uses QEMU Guest Agent to change network settings without rebooting. If the QEMU Guest Agent is unavailable for the platform for five minutes, VMmanager will reboot the VM to apply the settings.
To manage VM with CentOS OS, guest-exec function should be enabled in QEMU Guest Agent.
To avoid an unplanned reboot of the VM, you can check the status of the QEMU Guest Agent before changing the settings. This can be done on a VM or the cluster node.
Diagnostics
- Connect to the VM via SSH.
-
Define the status of the QEMU Guest Agent:
systemctl status qemu-guest-agentExamples of responses:
QEMU Guest Agent is running● qemu-guest-agent.service - QEMU Guest Agent Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/qemu-guest-agent.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Вт 2021-08-10 05:25:54 UTC; 1 weeks 3 days agoQEMU Guest Agent is stopped● qemu-guest-agent.service - QEMU Guest Agent Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/qemu-guest-agent.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) since Пт 2021-08-20 06:27:16 UTC; 2s agQEMU Guest Agent is not installedUnit qemu-guest-agent.service could not be found.
Restoring work
If QEMU Guest Agent is not installed
- Connect to the VM via SSH.
-
Install QEMU Guest Agent:
CentOSyum install qemu-guest-agentDebian, Ubuntuapt install qemu-guest-agent -
Add QEMU Guest Agent to the autostart:
systemctl enable --now qemu-guest-agent -
Check the status of QEMU Guest Agent:
systemctl status qemu-guest-agent -
Check the status of the SELinux service:
sestatusIf the status is different from disable:
-
Disable SELinux. Replace the below line in the /etc/selinux/config file
SELINUX=enforcingwith
SELINUX=disabled - Reboot the VM.
-
-
The file /etc/sysconfig/qemu-ga contains a line the below format
BLACKLIST_RPC=guest-file-open,guest-file-close,guest-file-read,guest-file-write,guest-file-seek,guest-file-flush,guest-exec,guest-exec-status- Mark this line as comment or delete it.
-
Restart QEMU Guest Agent:
systemctl restart qemu-guest-agent
If QEMU Guest Agent is stopped
- Connect to the VM via SSH.
-
Start QEMU Guest Agent:
systemctl start qemu-guest-agent
If guest-exec function is disabled
- Connect to the VM via SSH.
-
Run the command:
sed -i '/BLACKLIST_RPC=/cBLACKLIST_RPC=' /etc/sysconfig/qemu-ga -
Restart QEMU Guest Agent:
systemctl restart qemu-guest-agent
Running QEMU Guest Agent on Windows
Installation
- To prepare the VM for Virtio driver installation, create a 1 GB disk with Virtio connection type and connect it to the VM: Virtual machines section → select VM → Parameters button → Virtual disk → Connect one more disk → Create and connect a disk → select Size 1 GB and virtio Connection type → Connect the disk button.
- Download and install the Virtio drivers.
- For Windows Server 2012 R2 use virtio-win-guest-tools v.0.1.189.
- For Windows Server 2008 use virtio-win-guest-tools v.0.1.137.
- Download and install QEMU Guest Agent.
Diagnostics
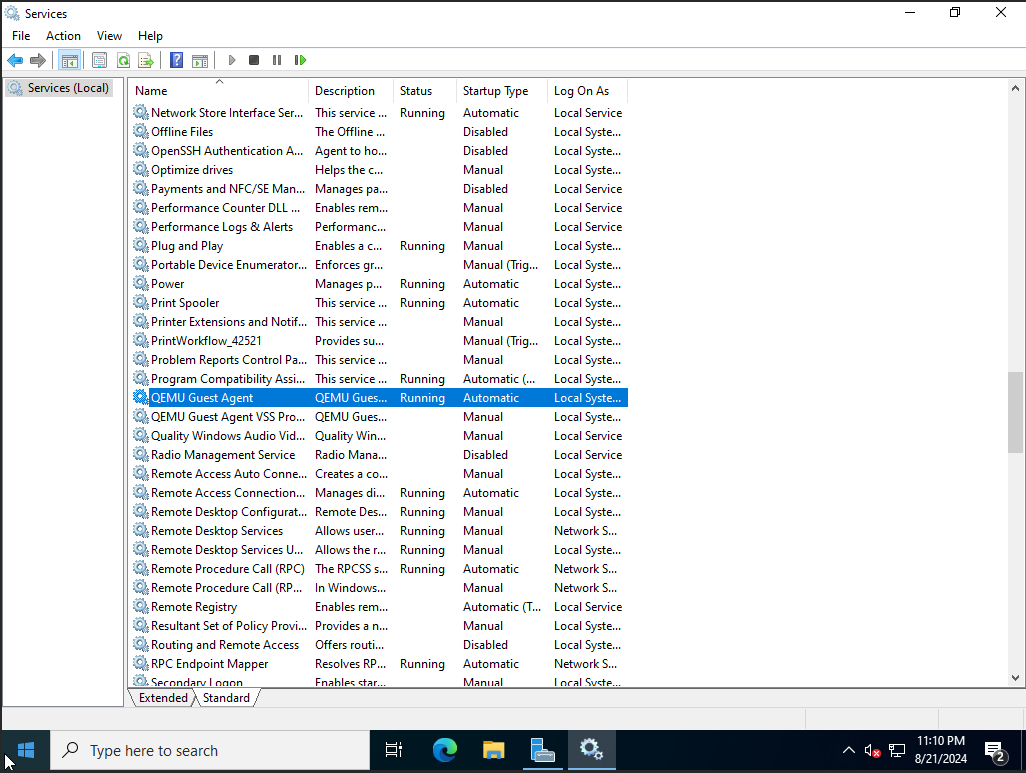
Run the services.msc service manager and check that QEMU Guest Agent is in the list of running services. If the service is stopped, start it. If the service is not listed, install the QEMU Guest Agent software.
 En
En
 Es
Es