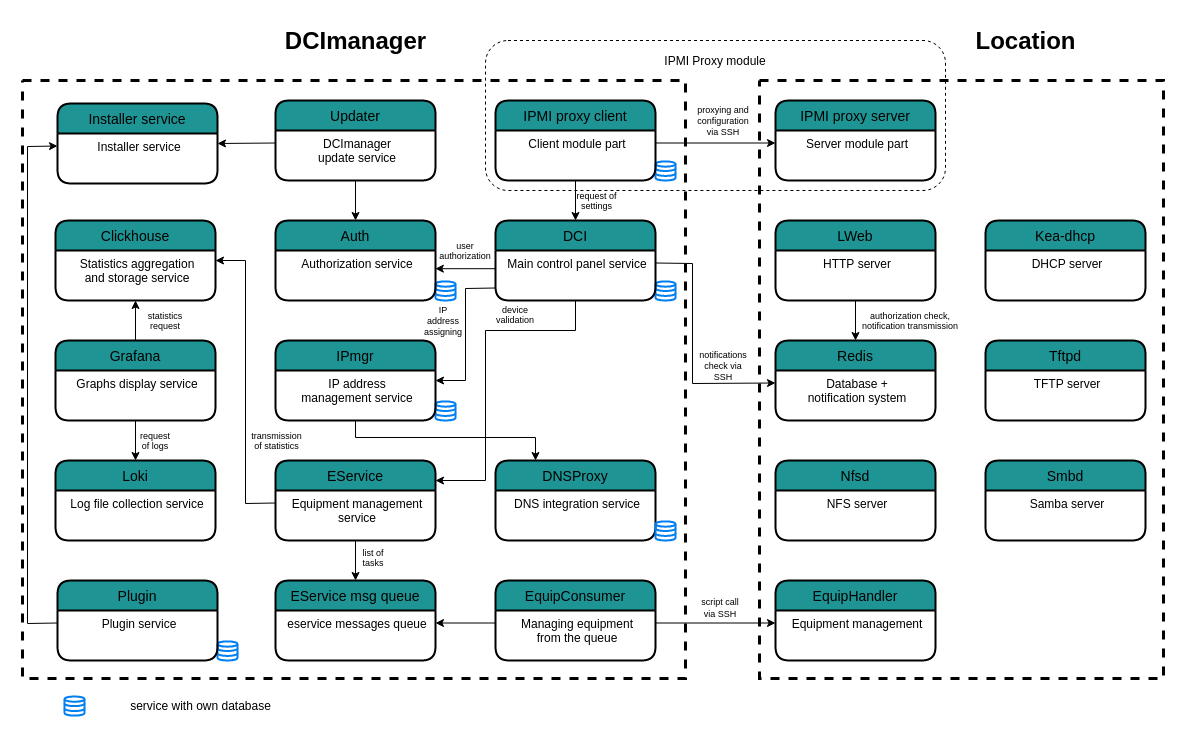
The architecture of DCImanager 6 is based on the use of Docker. The Docker technology allows to create and manage containers. A docker container is an isolated environment in which the application is running. DCImanager 6 uses the docker-compose service to manage all docker containers. The required environment is configured in the /opt/ispsystem/dci/docker-compose.yaml file.
DCImanager 6 containers
Container names may differ depending on the used version of Docker Compose. A hyphen may be used instead of the underscore character in container names.
To get the exact names of the containers, run the command:
docker ps -aThe following docker containers are started on the DCImanager 6 server:
- alert — container for platform notifications settings service;
- alert_wrapper — notification tracking service;
- auth_back — backend user registration and authorization service. Used for synchronization with the LDAP directory;
- auth_front — frontend user registration and authorization service;
- backup — platform backup service;
- batch — request sequence execution service;
- carbon_clickhouse — statistics aggregator;
- clickhouse_server — statistics storage service — Clickhouse database;
- consul — container for Consul service detection system. Read more about Consul in the official documentation;
- customizer — management of client service settings;
- dci_back — main container of platform backend;
- dci_front — main container of platform frontend;
- dns_proxy — container for working with Integration with DNSmanager 6 module;
- eservice — HTTP service for managing equipment;
- eservice_consumer — equipment management service;
- graphite_carbonapi — API service for transferring metrics to Grafana and the platform interface;
- graphite_clickhouse — service converting statistics data into graphite format;
- grafana — statistics visualization system;
- grafana_user — statistics visualization system for user servers;
- input — nginx server for request processing;
- ipmgr — IP addresses management service;
- ipmi_proxy_client — client part of BMC proxy module;
- journal — logging service;
- license — service responsible for receiving, updating and storing platform licenses;
- metric_collector — metrics collection service;
- migrator — DCImanager 5 migration service;
- msgsender — service for email sending to users;
- msg_queue — message queue for equipment management service;
- mysql or pgsql — container for working with MySQL;
- notifier — event tracking and notifications service;
- notice-center — service for sending notifications to the platform interface;
- plugin — plugin management container;
- report — report generating service;
- search — global search service;
- swagger — Swagger interactive shell;
- taskmgr — task manager service;
- telegram_srv - service for sending messages via Telegram;
- updater — DCImanager 6 update service;
- vault — storage of platform secret data (license, SSH keys, database key);
- vector_master — service for sending logs from Redfish BMC to Grafana;
- victoria_metrics — service for aggregating and storing metrics received from the OS agent;
- vmalert — service for sending notifications about exceeding storage equipment metrics.
The following docker containers are started on the location server:
- bird — routing service for the VPU module;
- eservice_handler — service containing equipment handlers;
- flow_msg_queue — temporary message queue storage for NetFlow statistics;
- goflow-1 — container for collecting NetFlow statistics;
- ipmi_proxy_v2_server — server part of BMC proxy module;
- kea_dhcp — DHCP server;
- lweb — HTTP server;
- nfsd — NFS server;
- redis — database and notifications system;
- smbd — SMB server;
- tftpd — TFTP server;
- vector_location — service for sending logs from Redfish BMC to Grafana;
- vmagent — service for collecting and sending metrics into the victoria_metrics storage.
Product operation logic
How to manage containers
Connect to the DCImanager 6 server via SSH and enter the command to view the list of running containers:
docker psTo enter the required container, enter:
docker exec -it container_name sh En
En
 Es
Es