Scripts allow you to set up virtual machines automatically: install software applications, modify configuration files, and perform other operations. You can:
- select a script when creating a virtual machine. It will be executed right after the operating system is installed;
- start a script on the existing virtual machine.
Scripts from the ISPsystem repository are available per default.
On a Linux OS, you can run Shell scripts in bash and sh, and on a Windows OS, you can run Powershell scripts.
You can set parameters for the script. Their values will need to be entered or selected from the list when running the script. Variables can be used as parameters to be entered manually. Then, when the script is run, the value of the variable will be displayed in the parameter input field.
ISPsystem scripts
By default, scripts from the ISPsystem repository are available in the platform:
- Bitrix Env — installing 1С-Bitrix: Web environment;
- Bitrix Env Crm — installing 1С-Bitrix: CRM;
- Django — installing Python framework Django with uwsgi and Nginx web servers, and MySQL DBMS. The script prepares the environment with the latest version of the framework. After installation, the Django web interface is available at http://<server IP>;
- ISPmanager Lite — installing website management panel ispmanager lite with the recommended set of software. After installation, the control panel is available at https://<IP server address>:1500/ispmgr. User name is root and the password is the server's root password;
- LAMP — installing Apache and Nginx web servers, MySQL DBMS, PHP software and phpMyAdmin. The root user password for MySQL is the same as the server's root password;
- LEMP — installing Nginx web server, MySQL DBMS, PHP software and phpMyAdmin. The root user password for MySQL is the same as the server's root password;
- Openvpn — installing the OpenVPN server. The script configures NAT and generates a client key in the directory /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/;
- Redmine — installing Redmine - a project and task management application. MySQL DBMS, web servers Nginx and thin are installed to run Redmine. After installation, the Redmine web interface is available at http://<server IP>; The user name is admin, the password is admin or the server root password (depends on the OS);
- Teamspeak — installing the voice communication server Teamspeak and control panel ts3-cp. After installation, the control panel is available at http://<IP server address>. Connection data are in the file /root/ts3_login_data;
- Tomcat — installing servlet containers Apache Tomcat. After installation, the server is available at http://<IP address of the server>:8080, the administration panel is available at http://<IP address>:8080/manager. The user name is admin and the password is the root password of the server;
- Wireguard VPN — Wireguard VPN installation. The client configuration is in the /etc/wireguard/client/client/client.conf file. The script does not configure access to the VPN;
- Zabbix installation. For more information, see the Zabbix article:
- Zabbix server — server installation;
- Zabbix proxy — proxy installation;
- Zabbix agent2 windows — agent installation for Windows;
- Zabbix agent2 linux — agent installation for Linux;
- Nagios installation. For more information, see the Nagios article:
- Nagios ncpa windows — installing the agent for Windows;
- Nagios ncpa linux — installing the agent for Linux;
- Route Reflector — install and configure the FRR daemon as a BGP Route Reflector. Running the script again adds "neighbors" and enables VxLAN support. See the IP fabric article for more details.
These scripts are closed for editing. You can create your own scripts based on them in the  menu → Copy.
menu → Copy.
Script restrictions
Command shell
The platform supports execution of Shell scripts only in bash and sh. If another shell is specified in the first line of the script (for example, #!/bin/dash), the script will terminate with an error. If the first line does not contain shell information, the script will run in the default shell (in most Linux systems it's bash).
Passing a password to the script
The value of the built-in PASS variable, which contains the root password, cannot be changed when running the script. Use your own variable or parameter to pass the password to the script.
VM reboot
If the script contains a reboot command, the script will be interrupted when the command is executed. The script will not continue running after the reboot.
OS Linux update
If a Shell script contains an OS update command, block the QEMU Guest Agent software update. This software provides execution of commands on VMs and information exchange between VMs and the cluster node. Updating the QEMU Guest Agent software can affect the platform's interaction with the VM.
yum -y update --exclude=qemu-guest-agentapt-mark hold qemu-guest-agent && apt-get update && apt-get -yy upgrade && apt-mark unhold qemu-guest-agentIf the update is run by external scripts:
-
Before the update commands, add lines to your script:
-
for Red Hat-based OS:
yum -y install yum-plugin-versionlock yum versionlock qemu-guest-agent -
for Debian-based OS:
apt-mark hold qemu-guest-agent || : apt-get update apt-get -yy dist-upgrade
-
- After the update commands, add lines to your script:
-
for Red Hat-based OS:
yum versionlock delete qemu-guest-agent -
for Debian-based OS:
apt-mark unhold qemu-guest-agent || :
-
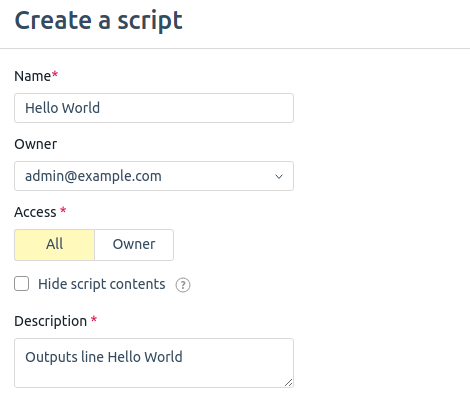
Creating a script
To create your own script:
- Go to Scripts section → For virtual machines tab → Create a script button.
- Enter a script Name.
- Select a script Owner. Only its owner can edit the script.
- Select who will have the Access to the image:
- Owner;
- All.
- If necessary, enable the Hide script contents option. Then only the owner of the script and platform administrators will be able to view the script code and create copies of it.
- Specify a Description. It is displayed in the script list.
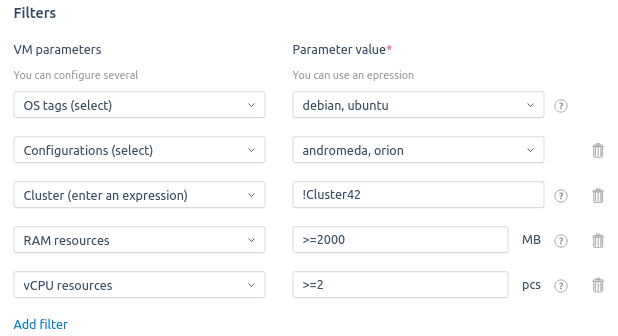
- Specify Filters to run the script. The script is available to run on a VM if the conditions of all filters match. The OS tags filter is mandatory, the others are optional. Read more in Filters for running scripts.
To add more filters, click Add filter button. To delete a filter, click the icon.
icon.
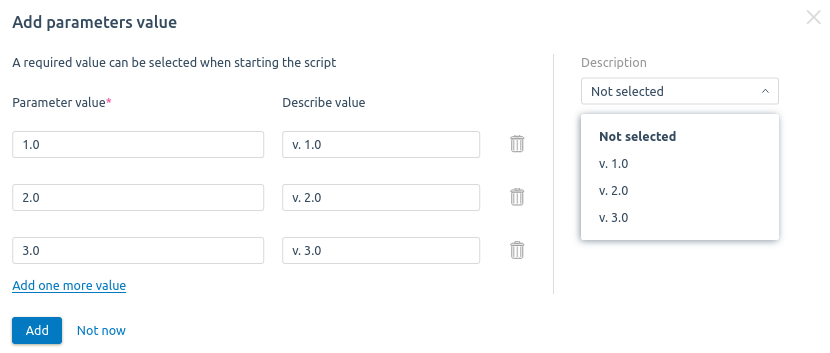
- If necessary, specify the requested script parameters:
- Click Add parameter button.
- Specify the parameter Name and Description. If you use a variable name as a parameter, its description will be added automatically.
- For a mandatory parameter, enable the Required option.
- To add more parameters to the script, click Add one more parameter to script button.
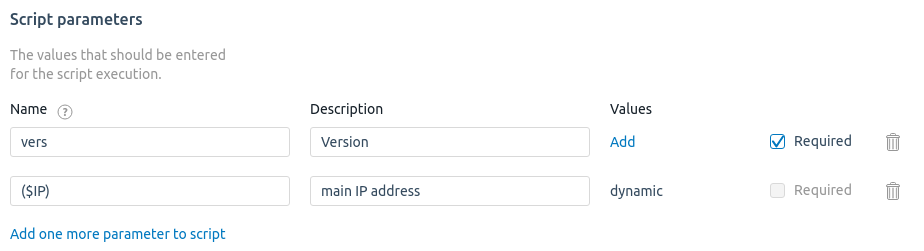
- You can specify parameter values that will be offered when the script is run. To do this, click Add button:
- Select a Script type:
- Shell — for Linux family OS;
- Powershell — for Windows OS.
-
Enter the Script in the editor window. To expand the editor window to the full screen, press
 . To return to the window mode, press
. To return to the window mode, press  . The editor has an auto-complete feature. For example, if you need to insert in a script the name of an external variable, start typing and the editor will suggest endings. External variables and parameters are specified in the script in the format ($NAME), where NAME is the name of the variable. For example, to write the VM IP address to a file, you can use the command echo ($IP) >> /tmp/ip.txt.
. The editor has an auto-complete feature. For example, if you need to insert in a script the name of an external variable, start typing and the editor will suggest endings. External variables and parameters are specified in the script in the format ($NAME), where NAME is the name of the variable. For example, to write the VM IP address to a file, you can use the command echo ($IP) >> /tmp/ip.txt.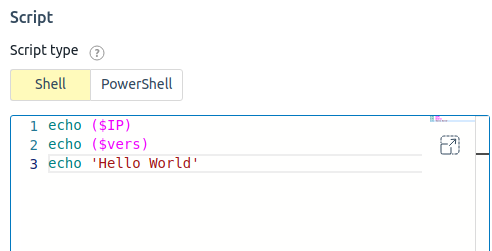
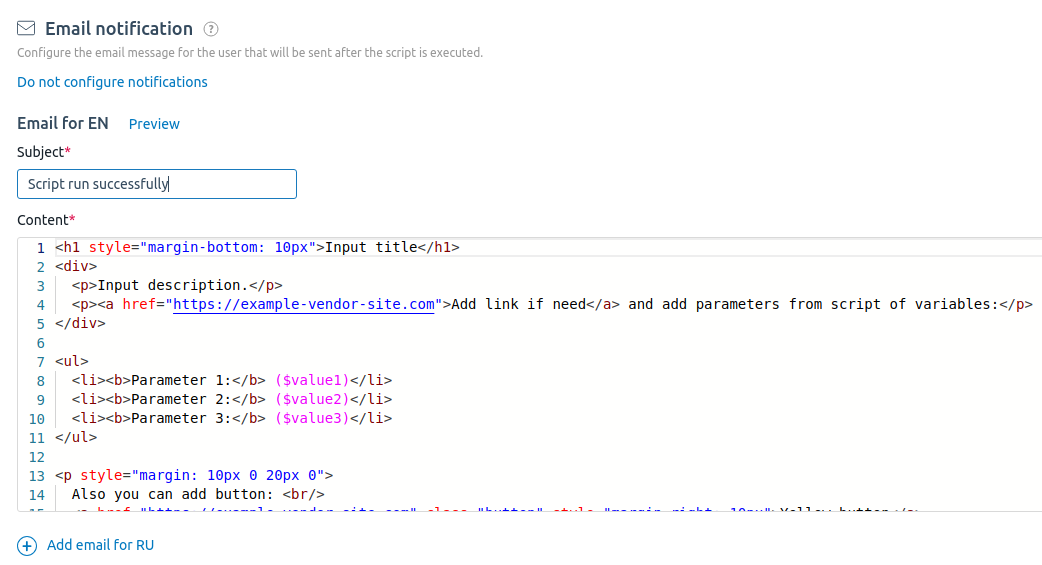
- To send an email to the user after running the script:
- Click Add button in the Email notification section.
- Enter the email Subject.
- Specify the content of the email in HTML format in the Content field. In this field, you can use the same variables and parameters that you used in the script. Read more about creating email templates in Email templates in scripts.
- Click Preview to preview the email.
- By default, you are offered to set up an English email template — Email for EN. If you need an email template in Russian, click Add email for RU button. If you no longer need any of the templates, click Delete the email for RU/Delete the email for EN button.
- Click Create button.
Operations with scripts
To manage scripts, go to the Scripts section → For virtual machines tab → select script →  menu. Possible actions:
menu. Possible actions:
- Copy — create a copy of the script;
- Edit (for custom scripts only) — change script settings;
- Informantion (for ISPsystem scripts only) — change the access settings of a script
- Delete (for custom scripts only).
To run scripts on a VM, go to the Virtual machines section → select VM →  menu → Run script → select scripts → enter script parameters → select the order of script execution in the Start priority column → Run scripts. Read more in the article Running scripts on the VM.
menu → Run script → select scripts → enter script parameters → select the order of script execution in the Start priority column → Run scripts. Read more in the article Running scripts on the VM.
To interrupt execution of the script, go to the Virtual machines section → select VM → in the Status column click the  icon next to the "Executing the script" message → Abort button. You can also interrupt script execution in the VM's task list: Virtual Machines section→ select VM → Parameters button → Tasks section → click the
icon next to the "Executing the script" message → Abort button. You can also interrupt script execution in the VM's task list: Virtual Machines section→ select VM → Parameters button → Tasks section → click the  icon in the "Execution of the script" task → Abort button.
icon in the "Execution of the script" task → Abort button.
- Running scripts on the VM
- Operations with virtual machines
- Variables for scripts
- Filters for running scripts
Knoledge base articles:
 En
En
 Es
Es