All operations performed in VMmanager can be divided into main and additional. Operations with a virtual machine launched in VMmanager are recorded to the log. Go to Virtual machines → open the VM page → History to view them. All active operations are represented on the tab Tasks.
Main operations
The main operations are available in Virtual machines →  menu or in Virtual machines → open a virtual machine page →
menu or in Virtual machines → open a virtual machine page →  menu:
menu:
- Start/Stop — start/stop a virtual machine;
-
Restart — restart a virtual machine;
Before a standard shutdown or restart of the VM, the platform tries to terminate running processes in the OS for 60 seconds.
You can perform a forced shutdown or restart of the VM. In this case, the platform will not wait for the running processes to complete. Forced shutdown and restart may result in loss of unsaved data.
To perform a forced shutdown or restart, start the operation and enable the Perform a quick forced shutdown of the VM (Perform a quick forced restart of the VM) option.
- Suspend — suspend the VM work. In this state the VM remains in RAM, but does not consume CPU resources. Any I/O operations for disks and network are blocked on such a VM;
- Resume — exit the VM from the suspended state;
- Reinstall — install a new operating system on your virtual machine:
- select an Operating system;
- select a Script to be launched upon operating system installation. Scripts help prepare virtual machines for operation. E.g. you can use them to install any software or set up configuration files. Read more in Scripts;
- specify the VM password. Click on Generate for an automatically generated password;
- Recovery mode — start/stop the recovery mode;
- Migrate — change the cluster node where the virtual machine is located. Read more in the article Migration of virtual machines;
- Console — go to the console of the LXD container. The console will open in a separate browser tab. Available only for VMs in LXD clusters;
- Change password — create a new root password for the virtual machine;
If a non-standard administrator name is used on a Windows VM, it will be changed to the standard one when the password is changed:
- for Windows Server — to
Administrator; - for Windows — to
admin.
- for Windows Server — to
- VNC — connect to the virtual machine desktop via VNC;
- SPICE — connect to the virtual machine desktop via SPICE;
- Create a snapshot — create a snapshot of virtual machine. Read more in Snapshots of virtual machines;
- Create backup copy — create a backup copy of virtual machine. Read more in Backups;
- Clone — create a copy of your virtual machine. Read more in Cloning of virtual machines;
- Create VM image — create a user image based on the disk of the virtual machine. Read more in Creating a disk image;
- Run script — select a script that will be started on the virtual machine via the SSH protocol. If necessary, specify the requested script parameters. To interrupt execution of the script, click
 in the VM card or the task queue;
in the VM card or the task queue; - Notes — add notes to a virtual machine;
- Protect VM/VM protection settings — enable/disable protection from basic actions. Read more in Protection of virtual machines;
-
Delete — delete a virtual machine.
In some cases, errors may occur when deleting VMs. For example, if the VM file on the cluster node was deleted, but the VM record remained in the platform database. To prevent these errors from blocking VM deletion, enable the Ignore errors when deleting option.
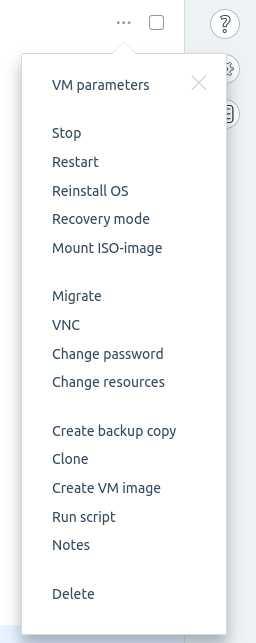
Additional operations
The additional operations are available in Virtual machines → open a virtual machine page.
Open the Information tab and click on Edit resources:
- vCPU (number of processors) in units;
- RAM in Mb;
- Storage in Mb.
You need to reboot your virtual machine to apply the changes in resources. Click on Edit and reboot to start rebooting, or click on Delay restart to do it later.
To change the owner of a virtual machine, open the Information tab, click Owner → edit → select a new one.
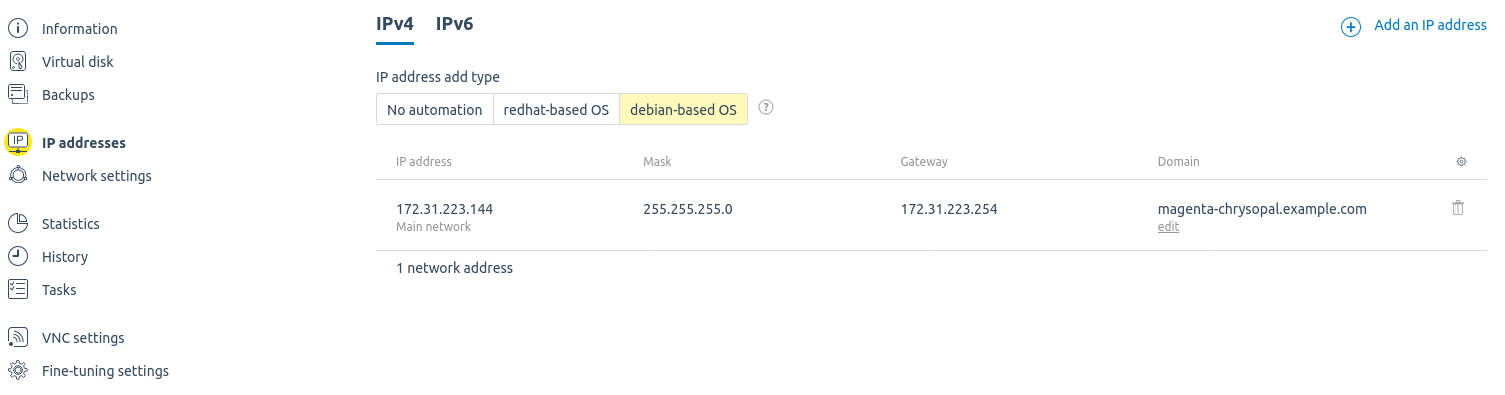
Use the tab IP addresses to see the IPs and domains assigned to your virtual machine:
-
click on Add an IP address to add a new IP. Select whether the address belongs to the Main or Additional network, the Number of IPv4 addresses and select a Pool that will be used to take the IP from. VMmanager will change the network settings in the VM operating system automatically.
NoteVMmanager does not change network settings for virtual machines running Windows. - click edit in the Domain column to change the domain name of the VM.
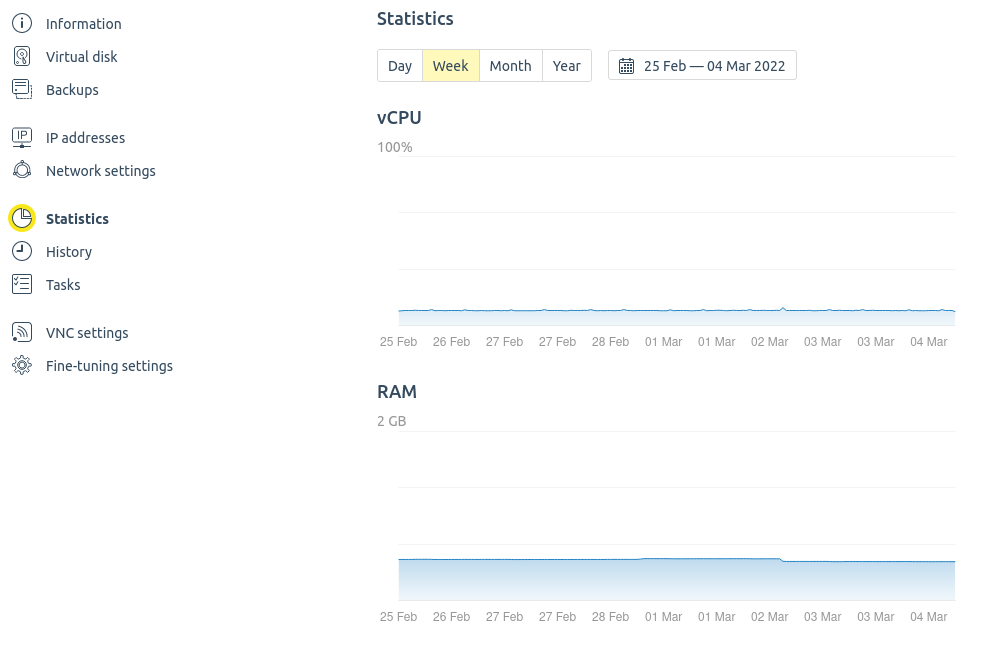
Open the Statistics tab to find the information about the resources consumed by the virtual machine. Here you can specify the period and the type of the resource:
- CPU load;
- RAM consumed;
- Storage consumed;
The Storage parameter shows how much the disk actually occupies on the cluster node at a given time:
- when using LVM storage, all the required disk space is allocated immediately;
- when using file storage, the VM disk will grow as it becomes full. However, when freeing up space on the VM disk, the disk size will not decrease.
In order for VMmanager to more accurately determine the amount of occupied space, QEMU Guest Agent software must be installed on a VM running a Linux or Windows family OS. For Windows OS VMs with multiple disks, we recommend using the QEMU Guest Agent version at least 103.0.0.
- Input-output operations (IOPS);
- Incoming traffic speed;
- Outgoing traffic speed. If the cluster has split traffic into external and internal traffic, you can select the type of traffic. Read more in the Networks management article.
If the VM is powered off, the statistics data is not displayed.
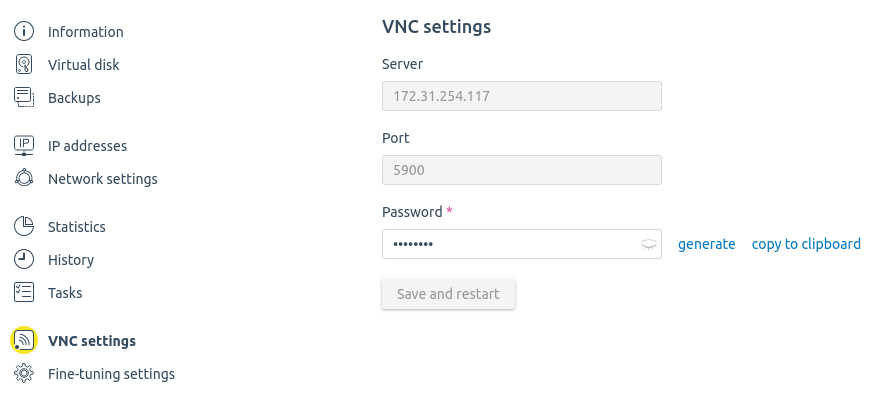
Use the tab VNC settings to view the data used to connect to a virtual machine via VNC:
- Server;
- Port;
- Password for access to a VNC server.
Read more in VNC.
Open the tab Images for recovery to see the list of disk images of the virtual machine which you can use as backup copies. A backup copy allows you to restore the state of the disk of your virtual machine.
- Click on Create an image to create a new disk image of the virtual machine. Read more in the article Creating a disk image.
- Click on Restore to delete the current virtual machine disk irreversibly and replace it with a disk from a backup copy.
Open the tab Fine-tuning settings to fine-tune parameters of the virtual machine. Read more in the article Fine-tuning of virtual machines.
 En
En
 Es
Es