A virtual machine (VM) is a software system that emulates the operation of a physical server. VMs are created and run on VMmanager cluster nodes. Each VM runs in an isolated environment and does not affect the other VMs on the node.
The platform supports two ways to create VMs:
- based on the recommended configuration — uses a ready-made set of resources and settings that can be changed if necessary. Read more in the Configurations of virtual machines;
- from an image — a VM disk image is used. Read more in the Creating a disk image.
Creating a VM based on the recommended configuration
To create a VM:
- Enter Virtual machines → Create a VM → Recommended configurations tab.
- Select the Cluster in which the VM will be created.
- Select the Operating system to be installed on the VM. To create a virtual machine without an operating system, click Without OS.
- To create a VM with the ISO image attached:
- Click Select an ISO image.
- Select a method for uploading the image:
- From repository — select the image from the connected repository;
- Local file — select the image file in iso format on your local computer;
- Image URL — enter the URL where the ISO image is available. The image can be available via HTTP(S) or FTP.
- To upload from a local file or URL:
- Select the OS type:
- Linux;
- Windows;
- FreeBSD;
- Other OS.
- Specify the Image tags for the connected OS if this VM needs to run scripts. The script will run on the VM if at least one of its tags matches the OS tag.
- Select the OS type:
- To avoid booting the VM from the image after connecting, disable the option Boot virtual machine from the ISO.
- Click Upload image. The VM will be created from NoOS template with the ISO image attached.
- Select the VM Resources from the list. To create your own configuration, click Custom configuration and specify its parameters. For the description of the parameters, see VM configurations.
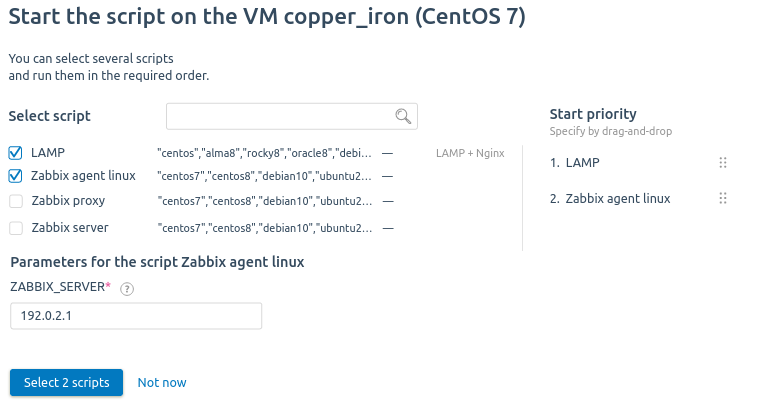
- Select the Applications and scripts that will run on the VM after the operating system is installed. Read more in Creating a script for the VM.
If an email template has been created for the selected script, you can enable the Send the email associated with the script option, select the language of the email and specify the recipient. Read more in Email templates in scripts.
To select multiple scripts: - Select the cluster Node to host the VM. If you select the Automatically option, the platform will detect the node taking into account the VM distribution settings in the cluster and the distribution filters. Read more in Selecting a cluster node for the virtual machine and Managing nodes in the cluster. If the VM configuration does not match the distribution filters for the cluster nodes, the creation of the VM will end with the error "Cannot find node with matching host filter program". In this case, select the node for the VM manually.
With the Automatically option, creating a VM with multiple network interfaces is not available. - If the cluster node was manually selected, configure VM disks distribution in storages of the cluster node. To change the location of the disk, drag it to the required storage location.

- Set the Network configuration for each VM interface. To change the settings for the main interface, click
 . To configure an additional interface, select its settings and click Add an interface. To delete an interface, click
. To configure an additional interface, select its settings and click Add an interface. To delete an interface, click  .
.
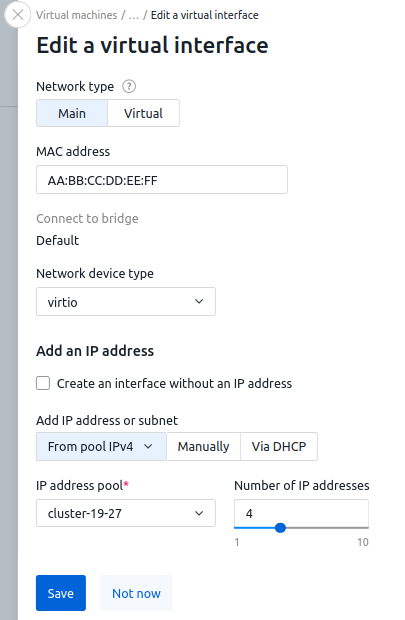
To configure the network interface:- Select a Network type:
- Main;
- Additional — available for clusters with two network interfaces. Read more in Main and additional network;
- Virtual — if a virtual network is available in the cluster. Read more in Virtual networks (VXLAN).
- If you need to set a specific MAC address for an interface, enter it. If the value is blank, the platform will generate the MAC address automatically.
- For main and additional networks:
- In the Connect to bridge field, select the bridge to which you plan to connect the interface. If there is only one bridge in the cluster, it will be selected automatically. A bridge is a network interface used on a cluster node. Each bridge can only be used on one virtual interface. Read more in the Network setting on the cluster node.
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- virtio — suitable for most operating systems;
- e1000 — for VMs installed from an ISO image;
- e1000e;
- rtl8139.
- To not assign an IP address to the interface on the main or additional network, enable the Create an interface without an IP address option. Anti-spoofing will be disabled on the VM with no IP address in order to work properly with the interface.
- Select how to Add IP address or subnet:
- From pool IPv4:
- Select an IP address pool from which to assign addresses to the VM.
- Select or enter the desired Number of IP addresses. A maximum of 10 IP addresses can be issued to a VM;
- From pool IPv6:
- Select an IP address pool from which to assign addresses to the VM.
- Enter the Subnet prefix from /32 to /125;
- Manually:
- Enter the IPv4 address or IPv6 subnet from the pool used in the cluster. For an IPv4 address, use the format
x.x.x.x.x, for an IPv6 subnet, use the formatx:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x/yy, where /yy is the subnet prefix from /32 to /125. If the address or subnet is not included in the pool used in the cluster, the VM will not be created;
- Enter the IPv4 address or IPv6 subnet from the pool used in the cluster. For an IPv4 address, use the format
- Via DHCP — The IP address will be provided by an external DHCP server. The platform will not consider this address, manage it and display it in the interface. You will be able to view the VM network settings only in the guest OS or DHCP server logs. The DHCP server must be correctly configured and be in the same L2 segment of the network as the VM.
If the VM's address is allocated via DHCP, antispoofing will be disabled on the VM for correct interface operation.
- From pool IPv4:
- In the Connect to bridge field, select the bridge to which you plan to connect the interface. If there is only one bridge in the cluster, it will be selected automatically.
- For virtual network:
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- virtio — suitable for most operating systems;
- e1000 — for VMs installed from an ISO image;
- e1000e;
- rtl8139.
- Select a VxLAN.
- Select a LAN.
- Select or enter the desired Number of IP addresses. A maximum of 10 IP addresses can be issued to a VM.
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- Click the Create (Save) button.
- Select a Network type:
- Set the VM Parameters:
-
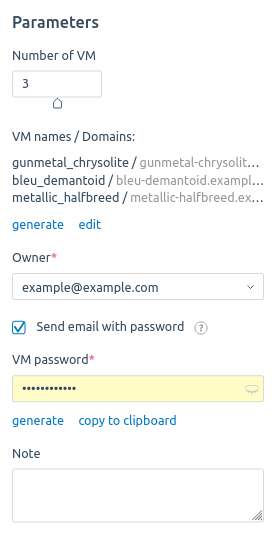
Select the Number of VM — from 1 to 5:
You cannot create more than one VM at a time with an ISO image attached.- when creating a single VM:
- Specify a VM name or click generate to automatically create a new one.
- Specify the Domain for the VM. A domain must have at least two parts separated by a dot. E.g., example.com.
- If two to five VMs are created, their names and domain names will be generated automatically. Click generate to automatically generate new names, or click еdit to enter names and domains manually.
- when creating a single VM:
- Select the VM Owner.
- To have the platform send an email with access details to the VM owner, enable the Send email with password option.
- Enter or generate the VM password. You can copy it to clipboard.
- Add a discretionary Note.
-
- Click the Create a VM button.
Creating from an image
Before creating a VM, prepare the required image. Read more in Creating a disk image.
To create a VM:
- Enter Virtual machines → Create a VM → VM images tab → select an image from the list.
- To create a linked clone, enable the create as linked clone option. Read more in the Linked clones.
- If you need to change the configuration, specify:
- vCPU — number of vCPUs, pcs;
- RAM — RAM size, MB;
- Storage — disk storage size, GB.
- Select the VM Owner.
-
Enter or generate the VM password. You can copy it to clipboard.
If a custom answer file was used when creating the Windows OS image, the VM password field will not be displayed. The VM will be created with the password from the answer file. Read more in the article Answer files for OS Windows images. - To have the platform send an email with access details to the VM owner, enable the Send email with password option.
- Select the cluster Node to host the VM. With the Select automatically option, the platform will determine the node taking into account the VM distribution settings in the cluster and the distribution filters. Read more in Selecting a cluster node for the virtual machine and Managing nodes in the cluster. If the VM configuration does not match the distribution filters for the cluster nodes, the creation of the VM will end with the error "Cannot find node with matching host filter program". In this case, select the node for the VM manually. With the Select Automatically option, creating a VM with multiple network interfaces is not available.
- If the cluster node was manually selected, select Storages for VM disks. Storage selection is not available if the VM image is in NAS.
- Set the Network configuration for each VM interface. To change the settings for the main interface, click
 . To configure an additional interface, select its settings and click Add an interface. To delete an interface, click
. To configure an additional interface, select its settings and click Add an interface. To delete an interface, click  .
.
To configure the network interface:
- Select a Network type:
- Main;
- Additional — available for clusters with two network interfaces. Read more in Main and additional network;
- Virtual — if a virtual network is available in the cluster. Read more in Virtual networks (VXLAN).
- If you need to set a specific MAC address for an interface, enter it. If the value is blank, the platform will generate the MAC address automatically.
- For main and additional networks:
- In the Connect to bridge field, select the bridge to which you plan to connect the interface. If there is only one bridge in the cluster, it will be selected automatically. A bridge is a network interface used on a cluster node. Each bridge can only be used on one virtual interface. Read more in the Network setting on the cluster node.
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- virtio — suitable for most operating systems;
- e1000 — for VMs installed from an ISO image;
- e1000e;
- rtl8139.
- To not assign an IP address to the interface on the main or additional network, enable the Create an interface without an IP address option. Anti-spoofing will be disabled on the VM with no IP address in order to work properly with the interface.
- Select how to Add IP address or subnet:
- From pool IPv4:
- Select an IP address pool from which to assign addresses to the VM.
- Select or enter the desired Number of IP addresses. A maximum of 10 IP addresses can be issued to a VM;
- From pool IPv6:
- Select an IP address pool from which to assign addresses to the VM.
- Enter the Subnet prefix from /32 to /125;
- Manually:
- Enter the IPv4 address or IPv6 subnet from the pool used in the cluster. For an IPv4 address, use the format
x.x.x.x.x, for an IPv6 subnet, use the formatx:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x/yy, where /yy is the subnet prefix from /32 to /125. If the address or subnet is not included in the pool used in the cluster, the VM will not be created;
- Enter the IPv4 address or IPv6 subnet from the pool used in the cluster. For an IPv4 address, use the format
- Via DHCP — The IP address will be provided by an external DHCP server. The platform will not consider this address, manage it and display it in the interface. You will be able to view the VM network settings only in the guest OS or DHCP server logs. The DHCP server must be correctly configured and be in the same L2 segment of the network as the VM.
If the VM's address is allocated via DHCP, antispoofing will be disabled on the VM for correct interface operation.
- From pool IPv4:
- In the Connect to bridge field, select the bridge to which you plan to connect the interface. If there is only one bridge in the cluster, it will be selected automatically.
- For virtual network:
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- virtio — suitable for most operating systems;
- e1000 — for VMs installed from an ISO image;
- e1000e;
- rtl8139.
- Select a VxLAN.
- Select a LAN.
- Select or enter the desired Number of IP addresses. A maximum of 10 IP addresses can be issued to a VM.
- Select a Network device type — virtual NIC model:
- Click the Create (Save) button.

- Select a Network type:
- Specify the Number of VM — from 1 to 5:
- when creating a single VM:
- Specify or generate a VM name.
- Specify the Domain for the VM. A domain must have at least two parts separated by a dot. E.g., example.com.
- If two to five VMs are created, their names and domain names will be generated automatically. Click generate to automatically generate new names, or click edit to enter names and domains manually.
- when creating a single VM:
- Click the Create button.
Access to a virtual machine
If the Send email with password option was enabled during VM creation, the platform will send an email with credentials to the VM owner.
The user name for connecting to the VM is taken from the OS template. Default values:
- for Unix family OS — root;
- for Windows family OS — Admin or Administrator.
Parallel VM creation
The platform can create multiple VMs simultaneously. There is a restriction on parallel creation of VMs with the same OS group on one cluster node. By default, no more than five such VMs can be created simultaneously. To change this value:
- Get the authorization token:
curl -k -X POST -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'https://domain.com/auth/v4/public/token' -d '{"email": "admin_email", "password": "admin_pass"}'Comments to the commandIn response, you will get the message in the form:
Example of response in JSON{ "confirmed": true, "expires_at": null, "id": "6", "token": "4-e9726dd9-61d9-2940-add3-914851d2cb8a" }Save the received token value.
-
Perform the API request:
curl -k -H "x-xsrf-token: <token>" -X POST "https://domain.com/vm/v3/setting/max_concurrent_host_create_tasks_per_node" -d '{"value":"<max_number>"}'Comments to the commandIncreasing this parameter will increase the load on the platform and cluster nodes.
 En
En
 Es
Es