Migration is the transfer of a virtual machine (VM) from one (source) node to another (target) node. VMmanager allows you to migrate VMs both within one cluster and to another cluster.
There are two types of migration:
- without VM stopping (live migration) — VM remains available during migration;
- with VM stopping — VM is unavailable for the time of migration.
Migration restrictions
For all types of migration
Migration cannot be performed if:
- the source node and the target node use different types of virtualization. For example, the source node is in a KVM cluster and the target node is in an LXD cluster;
- the source cluster has the Routing network configuration type;
- on a VM with Windows IP address adding model, QEMU Guest Agent is not installed;
- the VM uses a Route Reflector VLAN, which is not present in the targer cluster;
- an ISO image is connected to the VM;
- a VM uses vGPU.
For migration to a different cluster
Migration cannot be performed if:
- a Full Mesh VLAN has been created on the VM;
- clusters have different types of network configurations;
- source node and target node have operating systems from different Linux families. For example, the source node has Red Hat and the target node has Debian;
- VM disk is in NAS storage and migrates to storage other than file storage;
- high availability is configured in the source cluster or the target cluster.
If you migrate a VM with the Enable SPICE connections option to a cluster where SPICE connections are not allowed, the option will remain enabled, but SPICE connections will be unavailable.
For live migration
Migration cannot be performed if:
- the source or the target node has a QEMU version lower than 2.0.0;
- the version of QEMU on the target node is lower than on the source node;
- OS kernel version on the target node is higher than on the source node;
- a cluster node has nested virtualization enabled. Read more in the knowledge base article How to disable nested virtualization?
- the version of QEMU that was last used to run the VM is incompatible with the QEMU version on the target node. In such cases, it may help to synchronize the QEMU versions on the nodes and restart the VM before re-migrating;
- the source and the target node have the same UUID.
After live migration VM may freeze for the following reasons:
- CPU mismatch in Host-passthrough emulation mode;
- QEMU or libvirt error;
- OS kernel error.
For migration from VMmanager 5
The restrictions are listed in the article Migration from VMmanager 5 to VMmanager 6.
Work logic
Migration algorithm
- If live migration is not possible, the VM is stopped.
- A temporary directory is created in the storage with the VM disk to perform operations on the disk image to be copied.
- The XML description of the virtual machine is copied to the target server.
- If the Shrink the VM disk prior to migration option is enabled, the VM disk file is optimized. The optimization allows to get the minimum possible file size.
- The disk of the virtual machine is transferred:
- if the disk is in a local storage, it is copied to the target server; Live migration is performed using the virsh utility, while VM shutdown migration is performed using the dd utility with a block size of 1 MB. Therefore, live migration is usually faster.
-
if the disk is in a network storage, it is connected to the target server.
During live migration, QEMU periodically checks the state of the virtual machine during the migration. If the original VM data has changed, the copied data is overwritten by the changed data. If the virtual machine is in active use and data is constantly changing, migration will fail.
- if the disk is in a local storage, it is copied to the target server;
- The virtual machine and temporary directory are deleted on the source server.
- The virtual machine is started on the target server.
Bridge distrubution
For each VM network interface, the platform tries to find a suitable bridge on the target node. The following rules are used for bridge selection:
- Only the bridge of the main network can be selected for the main network interface, and only the bridge of the additional network can be selected for the additional network.
- A bridge is considered suitable if one of the conditions is met. The conditions are checked in the following order:
- The source interface bridge and the bridge on the target node have matching VLAN tags.
- The source interface bridge and the bridge on the target node are used by default.
- The source interface bridge and the bridge on the target node are not used by default.
- The source interface bridge and the bridge on the target node have the same names.
- No more than one VM interface can be allocated to each bridge on the target node.
After the interfaces are auto-allocated, the administrator can reallocate the interfaces manually on the migration form. If more than one interface of the source VM is distributed to any bridge on the target node, the platform will redistribute the interfaces during the migration process.
Starting the migration
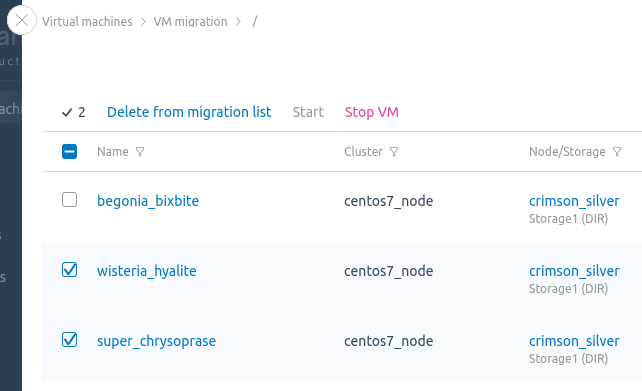
- Enter the Virtual machines section.
-
Select the VM →
 menu → Migrate or select the required VMs →
menu → Migrate or select the required VMs →  → Migrate.If migration is not available for all selected VMs, the menu item will contain the number of VMs available for migration. For example, Migrate (5).Group migration via the platform interface is available only for VMs located on a single cluster node. If you select VMs from different nodes, the group migration will be performed for the VM from the node that is higher in the list.
→ Migrate.If migration is not available for all selected VMs, the menu item will contain the number of VMs available for migration. For example, Migrate (5).Group migration via the platform interface is available only for VMs located on a single cluster node. If you select VMs from different nodes, the group migration will be performed for the VM from the node that is higher in the list.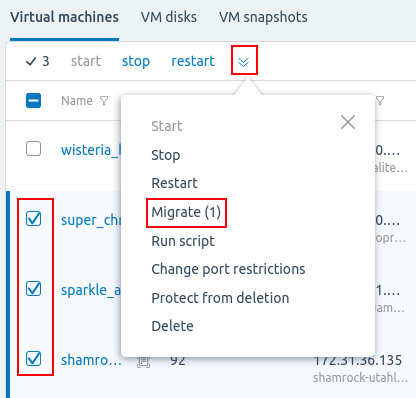
- To manage the list of VMs for migration:
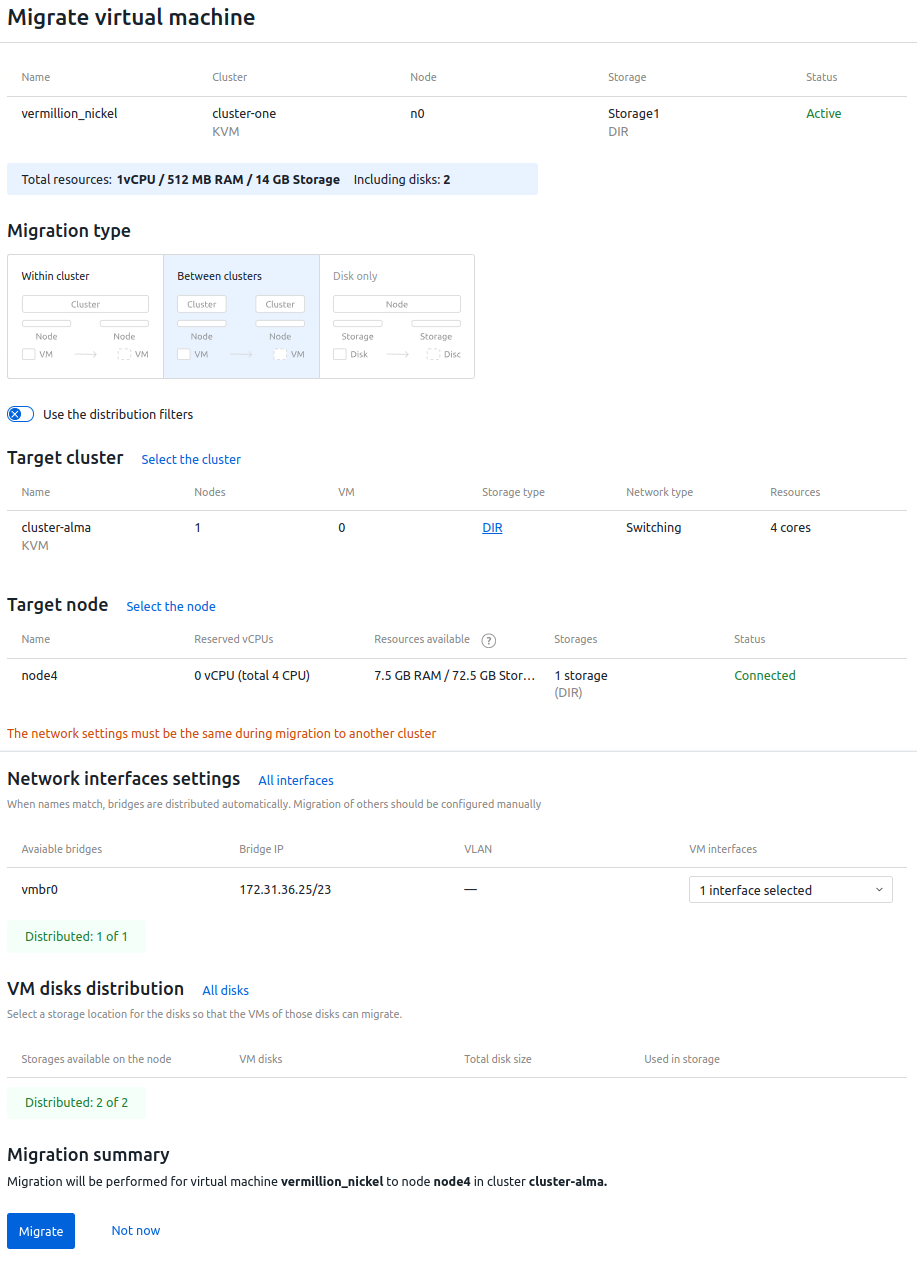
- Select the Migration type:
- Within cluster — VMs remain in the same cluster, but will be moved to a different node;
- Between clusters — VMs will be moved to another cluster;
- Disk only — VM disks will be moved to another storage.
- Specify the migration parameters:
- Disable the Shrink the VM disk prior to migration option if disk optimization is not required. The option is only available for disabled VMs.
- Disable the Use the distribution filters option if you do not need to use filters. Read more about distribution filters in Managing servers in the cluster.
- Disable the Cold migration of linked clones option if live migration of linked clones is required.
- To migrate Between clusters, in the Target cluster section, click Select the cluster and select the desired cluster from the list.
- To migrate Within cluster or Between clusters, in the Target node section, click Select the node and select the desired node from the list. If the node or live migration is unavailable, the Status column displays the reason for unavailability.
- In the Network interfaces settings section, select which interfaces on the target node will match the interfaces on the source node.
- In the VM disks distribution section, select in which storage the VM disks will be placed. Disks of the same VM can be placed in different storages.
- Explore the information in the VM resume section. The section contains information about whether all disks are allocated, whether VMs require rebooting, and whether VMs will be stopped during the migration.
- Click the Migrate button.
 En
En
 Es
Es