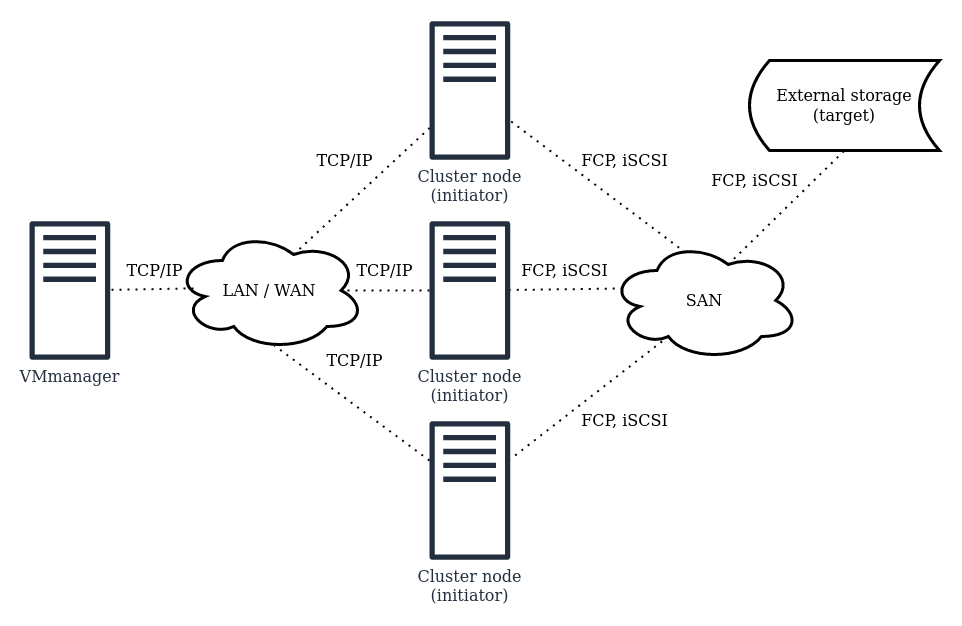
To connect LVM network storages, VMmanager uses SAN. SAN (Storage Area Network) is a technology for connecting external storage devices to servers. Server operating systems work with the connected devices as if they were local. SAN can be implemented using FCP (Fiber Channel Protocol), iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface), InfiniBand, AoE (ATA over Ethernet).
The main advantages of using a SAN:
- disk resources saving;
- easy management of disk devices;
- increasing the performance of disk devices;
- independence from LAN and/or WAN traffic;
- ability to back up data without creating extra load on the local network or servers;
- high performance, scalability and fault tolerance;
- ability to migrate virtual machines live.
The SAN uses the SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) protocol to transfer data. Network packets are transmitted via FCP (Fibre Channel Protocol) and iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) transport protocols.
Storage devices in a SAN are called targets and the servers that are connected to them are called initiators. When connecting an external storage, VMmanager cluster nodes act as the initiators, while the storage itself acts as the target. All cluster nodes work with storage as with a block device. For example, the storage can be connected as a /dev/sdb device.
Prior to creating a network LVM storage on the cluster nodes, some preliminary configuration is required. Read more in Pre-configuring SAN.
 En
En
 Es
Es