You can allow the platform users to log in only from specific IP addresses and subnets:
- Create user groups in the platform.
- Specify for each group the list of allowed IP addresses.
If the platform user is a member of the group and tries to log in from an IP address that is not listed in the group settings, the platform will block the user's access to the login service.
If the user is not a member of any of the groups, he/she can log into the platform from any IP address.
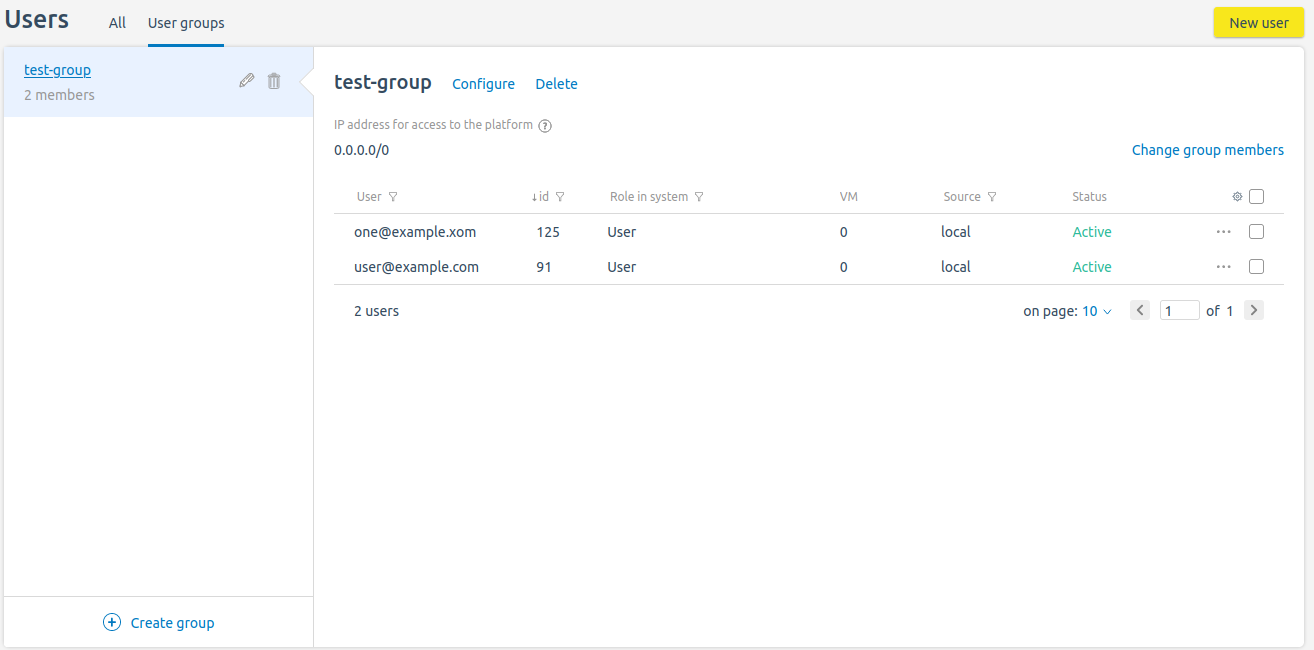
Managing user groups
To manage groups, enter Users → User groups.
Section interface
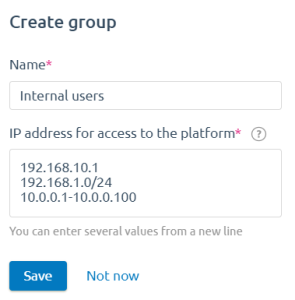
To create a group:
- Press Create group.
- Specify the group parameters:
-
- Name.
- IP addresses for access to the platform . The list can contain individual IP addresses, ranges and subnets of IP addresses.
- Press Save .
To change the settings of the created group, press  or Configure.
or Configure.
To delete a group, press  or Delete.
or Delete.
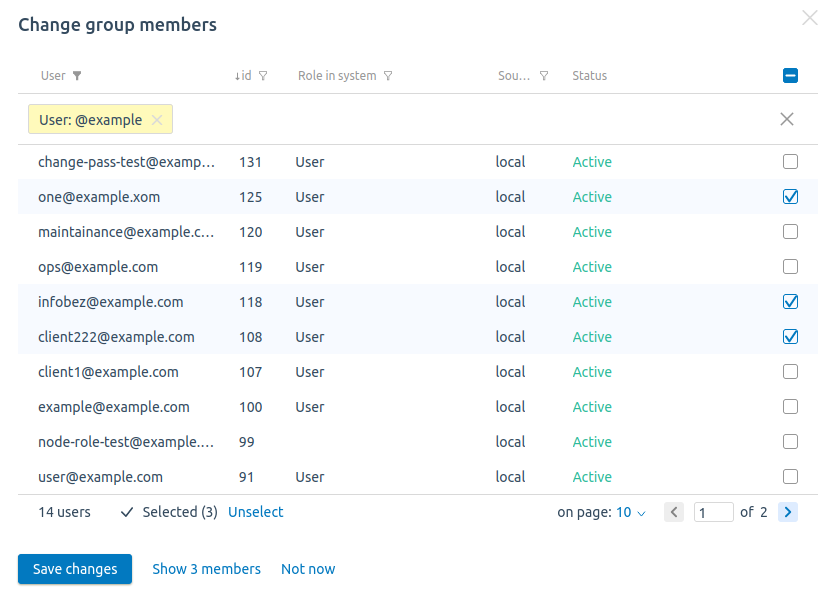
To add or delete users from a group:
- Press Change group members.
- Select the users you want to add.
- Uncheck the users you want to delete.
- Press Save changes.
Access control via API
The platform creates an access control list (ACL) for each user group. The ACL contains the group members' emails and lists of allowed IP addresses.
Creating an ACL
To create an ACL:
-
Get an authorization token:
curl -k -X POST -H "accept: application/json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'https://domain.com/auth/v4/public/token' -d '{"email": "admin_email", "password": "admin_pass"}'Comments to the commandIn response, you will get the message in the form:
Example of response in JSON{ "confirmed": true, "expires_at": null, "id": "6", "token": "4-e9726dd9-61d9-2940-add3-914851d2cb8a" }Save the received token value.
-
Execute the request:
curl -H 'x-xsrf-token: <token>' -X POST https://domain.com/auth/v4/acl -d '{"name": "<acl_name>", "ip_list": [<ip>], "members": [<users_id>]}'Comments to the commandNote:You can view the user IDs in the interface of the platform in the Users section.The response will contain the ID of the created ACL.
Example of creating an ACLcurl -H 'x-xsrf-token: 4-e9726dd9-61d9-2940-add3-914851d2cb8a' -X POST https://domain.com/auth/v4/acl -d '{"name": "admin1", "ip_list": ["192.0.2.1","192.0.2.10-192.0.2.20","192.0.2.100/28"], "members": ["1","3","7"]}'Comments to the exampleExample of response{ "id": "12" }
Viewing an ACL
To view all created ACLs, execute the request:
curl -H 'x-xsrf-token: <token>' GET https://domain.com/auth/v4/aclTo view a specific created ACL, execute the request:
curl -H 'x-xsrf-token: <token>' GET https://domain.com/auth/v4/acl/<acl_id>{
"ip_list": [
"192.0.2.1",
"192.0.2.10-192.0.2.20",
"192.0.2.100/28"
],
"name": "admin1",
"users": [
"user1@example.com",
"user3@example.com",
"user7@example.com"
]
}Deleting an ACL
To delete a specific created ACL, execute the request:
curl -H 'x-xsrf-token: <token>' -X DELETE https://domain.com/auth/v4/acl/<acl_id>If the ACL is deleted successfully, the response will contain "true".
If access to the platform is lost
If access to the platform is lost due to errors in the ACL settings, you can remove the ACL from the platform database:
- Connect to the server with the platform via SSH.
-
Connect to the platform database:
docker exec -it mysql bash -c "mysql <database> -p\$MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD"Comments to the command -
Perform the request:
select * from auth_user2acl;Example response+----+------+-----+ | id | user | acl | +----+------+-----+ | 3 | 122 | 4 | +----+------+-----+Save the values from the id and acl columns.
-
Perform the requests:
delete from auth_user2acl where id=<id>;delete from auth_acl where id=<acl>;Comments
 En
En
 Es
Es