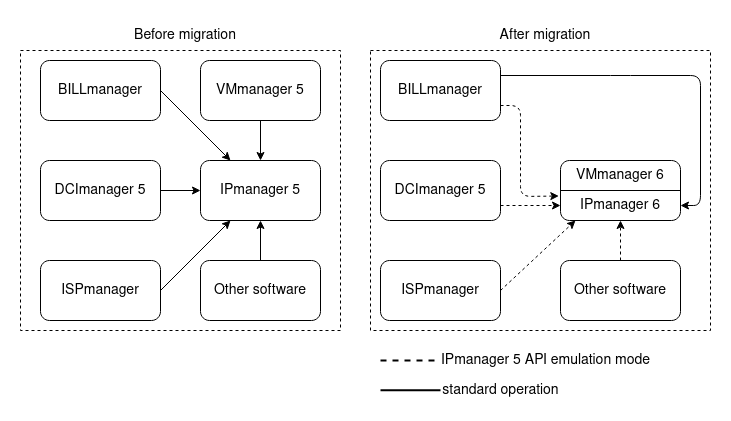
Migration allows you to move management of virtual machines (VMs) from VMmanager 5 KVM to VMmanager 6. Migration includes transfer of the following:
- address space — IP addresses, pools and networks used;
- user accounts;
- VM access restrictions;
- BILLmanager users, if the integration has been configured.
For migrated VMs, the platform will create a temporary cluster with limited functionality. After migration, you can migrate VMs from this cluster to other clusters in the platform.
Migration restrictions
You can transfer any cluster from VMmanager 5 to VMmanager 6. Further migration of VMs to VMmanager 6 clusters has limitations in the current version of the platform:
VM migration is possible to clusters with Switching or IP-fabric network settings.
Requirements for network settings
Each server must have a unique hostname.
Allow connections to the ports:
- between the server with the VMmanager 5 control panel and the VMmanager 6 platform:
-
- 22/tcp — SSH;
- 5900-6900/tcp — QEMU VNC, SPICE;
- 6514/tcp — libvirt virtual machine management service;
- 49152-49261/tcp — libvirt migration services;
- 443/tcp — HTTPS;
- between the VMmanager 5 cluster nodes and the VMmanager 6 cluster nodes:
-
- 22/tcp — SSH;
- 49152-49261/tcp — libvirt migration services;
- 443/tcp — HTTPS;
- between the VMmanager 5 cluster nodes and the VMmanager 6 platform:
-
- 22/tcp — SSH;
- 5900-6900/tcp — QEMU VNC, SPICE;
- 6514/tcp — libvirt virtual machine management service;
- 49152-49261/tcp — libvirt migration services;
- 443/tcp — HTTPS.
If integration of VMmanager 5 with IPmanager 5 or BILLmanager is configured, VMmanager 6 should have access to IPmanager5 or BILLmanager ports:
- 22/tcp — SSH;
- 443/tcp — HTTPS;
- 3306/tcp, 3306/udp - MySQL IPmanager or BILLmanager server;
If BILLmanager is located behind a DDoS protection service, specify the IP address of the BILLmanager server with ports 22/tcp and 443/tcp open in the migration settings. When migrating to BILLmanager, service and user IDs change, so VMmanager 6 can create many requests to BILLmanager, which may result in them being blocked by the DDoS protection.
Port 22/tcp must be available to all nodes in the cluster and, if necessary, to the public network.
If QEMU VNC, SPICE access is only provided through a server with VMmanager, the port range 5900-6900/tcp must be open to the network connecting the cluster nodes.
Migration procedure
Address space import
VMmanager 5 and VMmanager 6 use different software to manage the address space:
- VMmanager 5 uses the IPmanager 5 control panel;
- VMmanager 6 uses the built-in IPmanager 6 module.
IPmanager 6 supports IPmanager 5 API emulation mode. If you are using other software products that require integration with IPmanager 5 (for example, BILLmanager, DCImanager 5, ISPmanager), you can configure them to work with IPmanager 6.
VMmanager 5 cluster import
To import a VMmanager 5 cluster, the migration service:
- Connects to VMmanager 5 and gets information about the entities created in the control panel — VMs, users, cluster settings.
- Blocks VMmanager 5.
- Creates a backup of the VMmanager 6 platform.
- Imports information about VMmanager 5 settings into VMmanager 6.
- If integration with BILLmanager has been configured in VMmanager 5:
-
- Connects to BILLmanager.
- Changes the processing module type for VMmanager 6.
- Adds BILLmanager users with VMmanager 5 services to VMmanager 6.
Migrating users from VMmanager 5
If an e-mail is specified in the BILLmanager user settings, an account with that e-mail will be created in VMmanager 6.
If no e-mail is specified in the BILLmanager user settings, an account of the username@vm5.imported form will be created in VMmanager 6 where username is the VMmanager 5 user name.
Preparing for migration
VMmanager 5
- Create a backup of VMs and control panel. Read more in Backup plans in the VMmanager 5 documentation.
-
Enable public key authentication:
-
In the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, specify the parameter
PubkeyAuthentication yes -
Restart the sshd service:
systemctl restart sshd
-
-
Determine the number of CPU cores used on the cluster nodes:
dmidecode --type processor | grep -i "core enabled"
VMmanager 6
- Make sure that the VMmanager 6 license contains enough CPU cores to connect all cluster nodes from VMmanager 5. If necessary, purchase a license that supports more cores.
- If the platform is not installed:
- Make sure that the server for VMmanager 6 meets the system requirements.
- Install VMmanager 6 according to the manual.
- Perform initial setup of the platform.
BILLmanager
- Create a staff member to configure the integration. When creating, enable the Full access privileges option. Read more in the BILLmanager documentation article Departments and staff.
- Create the VMmanager 6 processing module and tariff plans for virtual server services.
- Create a backup of BILLmanager. Read more in Backup configuration in the BILLmanager documentation.
- Generate an authorization key:
- Connect to the server with BILLmanager via SSH with superuser permissions.
-
Execute the command:
/usr/local/mgr5/sbin/mgrctl -m billmgr session.newkey username='<integration_user>' key='<secret_key>'Comments to the command - Save the key value.
IPmanager 5
-
Make sure that IPmanager 5 is using the MySQL or MariaDB DBMS. If IPmanager 5 is using SQLite DBMS, switch to the use of MySQL DBMS. Read more in Usage of MySQL as a DBMS (database management system).
NoteThe recommended MySQL/MariaDB version is at least 5.5.x. For earlier versions, successful VM import is not guaranteed. - Make sure that the MySQL server is accessible from VMmanager 6 — check if ports 3306/TCP, 3306/UDP are open in the firewall settings and if remote connection to the database is possible:
- Connect to the IPmanager 5 server via SSH.
-
Check the current firewall settings:
firewall-cmd --list-all -
Open ports 3306/TCP, 3306/UDP:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/udp -
Restart the firewall service:
service firewalld restart -
Open the MySQL configuration file /etc/my.cnf. Add the bind-address=xxx.xxx.xx.xx paramter to the [mysqld] section and mark as comment the line with the skip-networking parameter.
Comments -
Connect to mysql service:
mysql -u rootuse mysql; -
Allow the user to connect to MySQL remotely:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON <DB_NAME> . * TO '<DB_USER>'@'<REMOTE_IP>' IDENTIFIED BY '<DB_PASSWORD>';CommentsFLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Migration
IP address migration
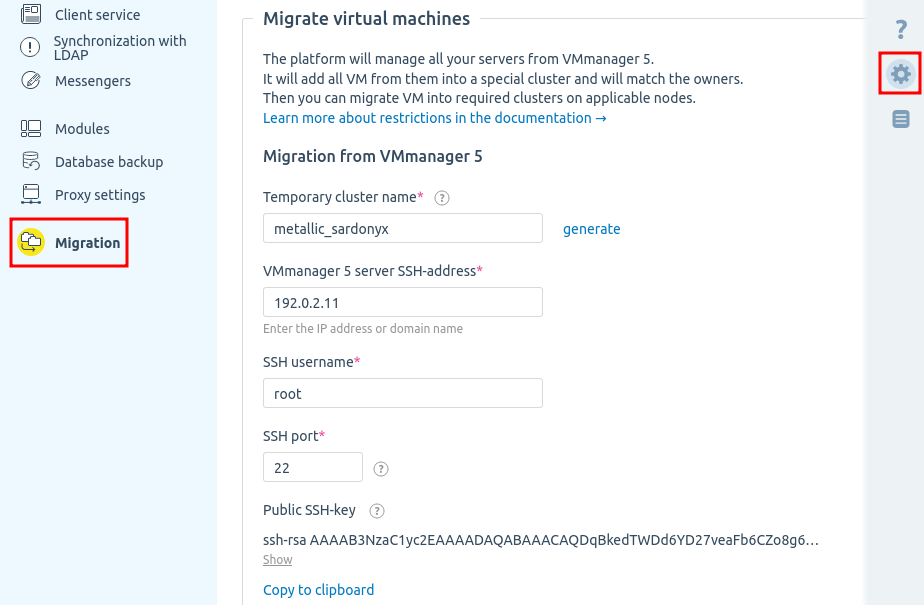
- Enter
 → Migration → Migrate IP addresses from IPmanager 5.
→ Migration → Migrate IP addresses from IPmanager 5. -
Specify the connection settings for IPmanager 5:
NoteThe connection settings are specified in the IPmanager configuration file /usr/local/mgr5/etc/ipmgr.conf :
- Address of server with IPmanager — DBHost parameter;
- Database name — DBName parameter;
- Integration user login — DBUser parameter;
- Password — DBPassword parameter.
- Address of server withi IPmanager — IP address of the IPmanager 5 database;
- Database name — IPmanager 5 database name;
- Integration user login — IPmanager 5 database username;
- Password — IPmanager 5 database user password.
- Press Migrate IP.
How to migrate separate blocks of IP addressesTo enable VMmanager 5 and BILLmanager to work with IPmanager 6:
- To allow VMmanager 5 to access only a certain pool of IP addresses, create a pool in VMmanager 6 with the suffix public. For example, VM5_public.
-
Create an administrator account named ipmgr5@example.com in VMmanager 6.
Noteipmgr5@example.com is not an example, but the exact name that you need to specify when creating an account. - In VMmanager 5 and BILLmanager:
- Enter Integration → IPmanager .
- Specify the settings for integration:
-
URL — https://domain.com/api/ipmgr5/v3/ipmgr
Comments to the URL -
Username:
-
to allow the control panel to access only a certain pool of IP addresses, specify pool_XXX;
Comments - to allow the control panel to access the entire address space, specify an arbitrary user name.
-
- Password — password of the ipmgr5@example.com user.
- In the Synchronization of IP-addresses section leave the Administrator login and Administrator password fields blank.
-
- Press Ok.
If VMmanager 6 has integration with DNSmanager 6, you need to synchronize PTR records with the DNS-server after the address space is created. To do this:
- Delete the DNSmanager 6 integration module: Settings → Modules → Integration with DNSmanager 6 → Delete the module → Delete the module.
- Reinstall and configure the integration module. Read more in Integration with DNSmanager 6 module.
You can check the success of synchronization in the /var/log/dns_proxy_integration.log file in the vm_dns_proxy_1 container on the server with VMmanager.
Virtual machines migration
NoteYou can migrate virtual machines from multiple VMmanager 5 instances to a single VMmanager 6 instance. A separate temporary cluster will be created for VMs from each VMmanager 5 instance.- Enter
 → Migration → Migrate VMmanager 5.
→ Migration → Migrate VMmanager 5. - Specify the migration settings:
-
Copy the Public ssh-key and add it to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the server with VMmanager 5.
NoteTo enable public key authentication, in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file on the server with VMmanager 5, specify the parameter
PubkeyAuthentication yes - Specify the settings of connection to BILLmanager if integration has been set up in VMmanager 5:
- BILLmanager 5 server address — server IP address or domain name.
- Panel administrator login — name of the staff member created when preparing BILLmanager.
- Temporary key created during BILLmanager preparation.
- VMmanager 5 handler name.
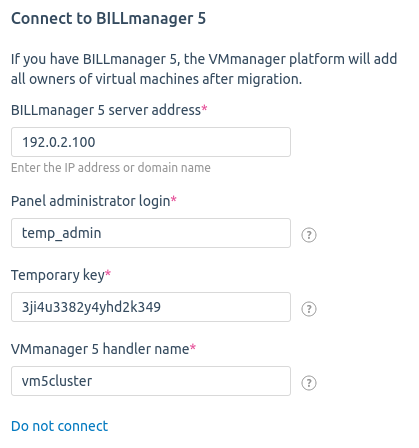
- Press Migrate VMmanager 5.
If the migration failed with an error of the following form
{ "error": { "code": 1111, "msg": "Handler throw uncaught exception", "value": "vm/import/cluster Can not load a vm5_data file" } }check whether an SSH connection is available from the vm_box containter in the VMmanager 6 server to the main VMmanager 5 node.
The IP address of the main VMmanager 5 node is specified in the MainIp parameter of the /usr/local/mgr5/etc/vmmgr.conf configuration file on the server with VMmanager 5.
Transferring a VM from a temporary cluster
A temporary cluster is created for VMs from VMmanager 5 with the VM5 KVM type and "Switching" network configuration. Available operations with VMs in a temporary cluster:
- power on;
- power off;
- reboot;
- connection via VNC or SPICE;
- delete;
- migrate to another cluster node;
- migrate to another cluster, if the VM configuration meets the requirements.
To ensure that all functions are available on migrated VMs, migrate them to other platform clusters.
If a VM does not meet the requirements for migration to the VMmanager 6 cluster, the Migration to the VM6 cluster is unavailable link is displayed next to its name. Click on the link for more information.
If the VM has network interfaces connected to NATIf the VM has snapshotsIf ISO images are connected to the VMIf the VMmanager 5 node is running CentOS 6If the VM's IP address adding model is "No automation"To properly migrate VMs with Windows operating systems, install the libguestfs-winsupport utility on the temporary cluster node.
The platform interacts with the VM through the QEMU Guest Agent program. For example, QEMU Guest Agent is needed so that VMmanager can change the password or run the script on the VM. If QEMU Guest Agent is not installed on the VM or is not responding, the Status column displays the message Problem with Guest Agent. To install QEMU Guest Agent on a VM, click on Problem with Guest Agent → Install GA and restart VM. You can install QEMU Guest Agent manually. For more information, see the knowledge base article How to check and restore QEMU Guest Agent?
If the name of the VM's network interface has not been defined, the interface will be saved with the no_name suffix. If there is more than one such interface, the QEMU Guest Agent must be installed on the VM to migrate to a VMmanager 6 cluster.VM migration without powering it off ("live" migration) is possible if:
- QEMU version 2.0.0 or higher is installed on the VMmanager 5 cluster node;
- the version of libvirt on the VMmanager 6 cluster node is not lower than the version of libvirt on the VMmanager 5 cluster node.
In other cases, the VMs must be powered off before migration.
To move a VM from a temporary cluster:
- Select the necessary VMs → more... → Migrate.
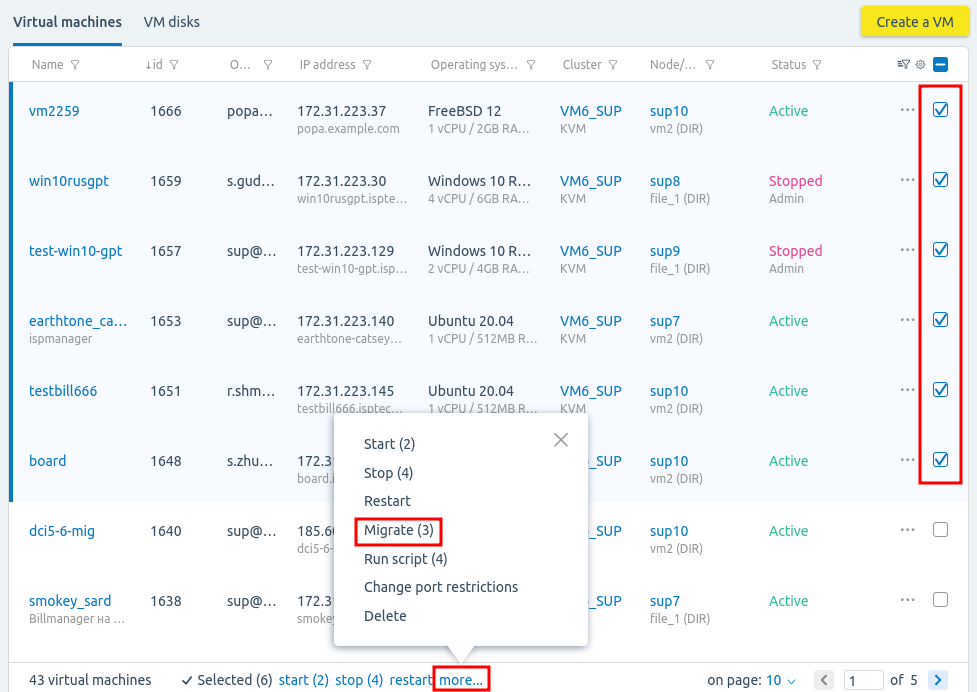
- Specify the migration settings:
- Disable the Shrink the VM disk prior to migration option if disk compression is not required. The option is only available for disabled VMs.
- Disable the Use the distribution filters option if you do not need to use filters. Read more about distribution filters in Managing nodes in the cluster.
- Select the cluster to migrate to.
- Select the node to migrate to.
- Select the available storages on the node that will host the disks of the VMs. Disks of the same VM can be placed in different storages.
- Review the information in the VM Summary section. The section contains information about whether all disks are allocated and whether the VM needs to be rebooted.
- Press Migrate (Migrate and reboot).
What to do after migration
After VMs migration, a temporary cluster can be deleted. Free nodes from the temporary cluster can be connected to other clusters in the platform. We recommend that you reinstall the OS on these nodes before connecting.
Transferring services in BILLmanager
If integration with BILLmanager has been configured in VMmanager 5, then the migration service will:
- Change the processing module type from VMmanager 5 to VMmanager 6.
- Add the prefix _imported to its name.
A new processing module is created to manage the VMs in the temporary cluster. Ordering new services through this processing module is not available. After migrating the VMs to other platform clusters, switch the services to tariff plans with a different VMmanager 6 processing module.
To manually migrate services to a new processing module:
- Connect the VMmanager 6 service processing module for VMmanager 5 tariff plans:
- Enter Products → Tariff plans → select the tariff plan from which the virtual server service for VMmanager 5 was sold → Modules button.
- Enable the VMmanager 6 processing module.
- Power the virtual machines off from BILLmanager:
- Enter Products/Services → Virtual private servers → select all VMmanager 5 virtual server services (press CTRL) → Edit button.
- Press the Disable button.
- Confirm powering off with the Ok button.
- Migrate virtual server services to tariff plans with the VMmanager 6 processing module:
- Enter Products/Services → Virtual private servers → select all VMmanager 5 virtual server services (press CTRL) → Edit button.
- Specify the VMmanager 6 service processing module in the Processing module field.
- Press Ok .
- Enable the services in BILLmanager.
- Delete the staff member created for integration.
Possible issues
Possible migration issues are described in the Knowledge Base article Possible issues with migration from VMmanager 5.
Re-migration
If the first migration failed, you can perform the migration again. If an address space was imported during the first migration, you do not need to delete it to migrate again.
To migrate services from BILLmanager, re-generate the authorization key.
Canceling migration
You can return VM management to VMmanager 5 after migration. Migration can be cancelled only if the VMs were not deleted or moved to other clusters after migration.
To cancel migration:
- Restore the status of VMmanager 6 from a backup. Read more in Creating platform backups.
- If you changed BILLmanager settings, restore the control panel from a backup. Read more in Backup configuration in the BILLmanager documentation.
- Unlock VMmanager 5:
-
- Connect to the server with VMmanager 5 via SSH:
-
Execute the command:
/usr/local/mgr5/sbin/mgrctl -m vmmgr -u
 En
En
 Es
Es