VAT (Value Added Tax) — is a value added tax in the European Union (EU).
VAT is charged on both physical and digital goods and services. The EU Directive dated January 1, 2015 contains the complete information on regulation of VAT for digital products.
What belongs to digital products
A digital product is a product or service that is provided to the user in electronic format. The provision of such products is automated, requires minimal human intervention and is impossible in the absence of information technologies.
The list of the most common goods and services that belong to digital products includes:
- software and associated updates;
- cloud computation platforms;
- website hosting;
- remote service of software and equipment.
The full list of digital products is provided at the EU website.
In which cases VAT is charged
It is important for companies to consider two factors in order to determine when to collect VAT: from which country their clients are and whether they are companies or individuals.
Provision of digital goods and services can be displayed within the following frameworks of relationship:
- B2B (Business-to-business) — a company sells its goods/services to another company;
- B2C (Business-to-consumer) — a company sells its goods/services to end consumers.
The company and its clients may be located both in the EU and outside the EU. The logic of VAT assignment will change accordingly. The diagram below shows the possible options.
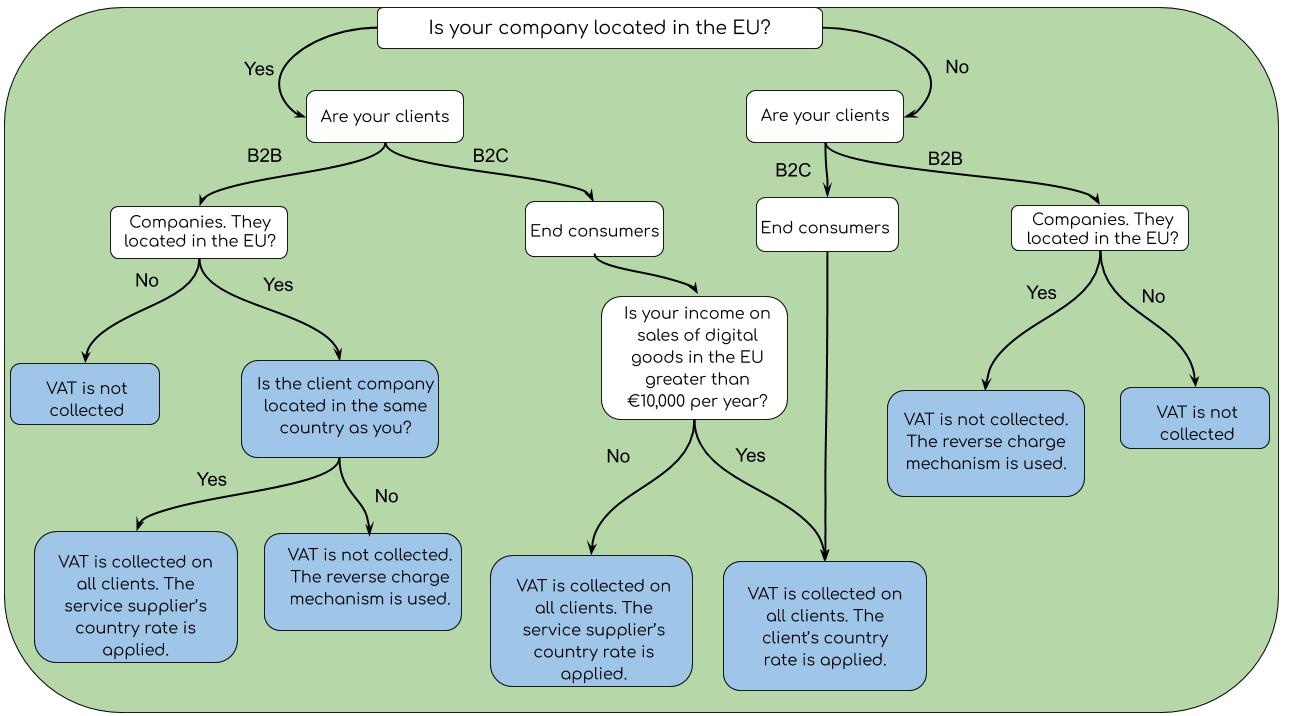
VAT assignment options
Under European Union law, VAT must be collected from all consumers of goods/services from EU countries. If EU citizens purchase goods or services from companies from other countries, VAT must also be paid. Companies from non-EU countries should take this factor into account and work properly with the EU tax system.
How to start working with VAT
The process of working with VAT in the European Union can be presented in a few steps.
Step 1. Register a company with a VAT number
Register your company with the EU tax authorities and get a VAT number. The VAT number allows you to sell goods and services to clients from EU countries.
If you provide goods or services to citizens from one EU country, all you have to do is register with the tax authority of that country and collect VAT at the current rate.
If you provide goods or services in several EU countries, you need to register with the tax authorities of each country where you have customers or in the MOSS (Mini One-Stop Shop) system. The MOSS system was established in 2015 to simplify VAT payments for digital goods. When registering in this system, you do not need to register with the tax authorities of each of the countries where you have clients, and registration with MOSS of any of the EU countries is sufficient.
Step 2. Determine who your clients are and which country they are from.
To meet EU requirements and submit correct tax reports, two factors must be taken into account:
- Determine whether your client is an individual or a legal entity. Every legal entity must have a valid VAT number and this number must be checked every time you pay. If there is no such number, the client is considered an individual.
- Determine the client's location. Correct determination of the client's country governs the assignment of the correct tax rate.
Step 3. Include VAT in the price of your goods
Add VAT to the price of your goods. The price of the goods or service, including VAT, must be shown automatically to each client. Meanwhile, the VAT amount should be calculated based on the client type and location. In BILLmanager you can use a special VAT module for companies with a European Union VAT number. The module adapts the billing system to VAT accounting for EU payers. Read more in How to install and configure the VAT module.
Step 4. Keep all VAT invoices
Every sale to EU clients must be accompanied by a VAT invoice. For B2B sales, where no VAT is charged, a special VAT invoice form is used.
The European VAT invoice must include:
- name and address of your organization;
- your company's VAT number;
- invoice date;
- invoice number;
- client’s name and address;
- client's VAT number.
- statement regarding reverse charge mechanism;
- VAT rate;
- VAT amount;
- total price including VAT.
In BILLmanager, when connecting the VAT module for payers from EU countries, the EU credit invoice template is added.
Step 5. Submit reports to tax authorities
Within 20 days after the end of each quarter, reports must be submitted to the EU tax authorities or the MOSS system.
When registering in the MOSS system, you need to submit VAT returns to the MOSS of the country where you are registered through the system’s website. On the website, you specify information about the countries to citizens of which you provided the service. The system will calculate the VAT that you must pay. You pay the entire invoice to MOSS and the system transfers the VAT to other EU countries on your behalf.
If you are not registered with MOSS, you will need to contact the tax authorities of each country separately.
Reverse charge mechanism
The reverse charge mechanism is used for VAT accounting when providing goods and services under the B2B scheme. It consists in the fact that the obligation to pay VAT is imposed on to the client. By using this mechanism, you do not need to be an intermediary in receiving VAT between the client and the state. The client pays the tax directly to the state.
If your company provides services to legal entities, you need to specify in the invoice that reverse charge mechanism is used, and provide the valid VAT number of your client.
 En
En
 Es
Es